Page 90 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 90
74 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
different concentrations of fluorocarbon polymer Zonyl8740 solution is
taken as the measuring matrix.
2. Experimental Method
The glass slide is first washed with ethyl alcohol and then with dis-
tilled water. After drying under high pressure nitrogen, it is immediately
put into Zonyl8740 solutions of varying concentrations before it is
taken out, sealed, and dried after soaking for 4 hours. Contact angle of
air bubble and n-octane with water is measured with a contact angle
meter under an atmospheric pressure at 20 C. The size of bubbles and
liquid drops are all 5 μL.
3. Experimental Result and Discussion
The glass slide/water interface free energy (γ glass slide-water ), free energy
(γ glass slide ) of glass slide surface, and work of adhesion (A) in the bub-
ble capture method can be obtained by combining the values obtained
from indoor experiments of contact angles of bubbles of glass slide trea-
ted with Zonyl8740 solutions of varying concentrations and liquid in
distilled water, and the theoretical derivation in Section 4.2.2. See
Table 2.14 for the contact angle measured from experiments and calcu-
lated interface free energy.
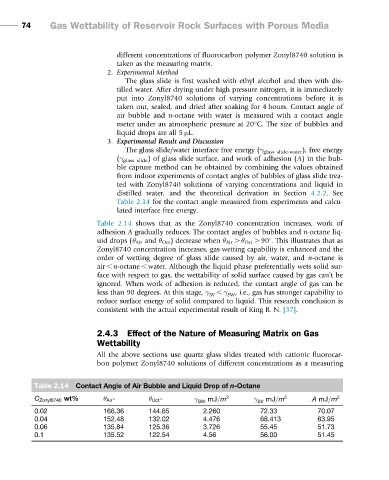
Table 2.14 shows that as the Zonyl8740 concentration increases, work of
adhesion A gradually reduces. The contact angles of bubbles and n-octane liq-
3
uid drops (θ Air and θ Oct ) decrease when θ Air . θ Oct . 90 . This illustrates that as
Zonyl8740 concentration increases, gas-wetting capability is enhanced and the
order of wetting degree of glass slide caused by air, water, and n-octane is
air , n-octane , water. Although the liquid phase preferentially wets solid sur-
face with respect to gas, the wettability of solid surface caused by gas can’tbe
ignored. When work of adhesion is reduced, the contact angle of gas can be
less than 90 degrees. At this stage, γ SV , γ SW , i.e., gas has stronger capability to
reduce surface energy of solid compared to liquid. This research conclusion is
consistent with the actual experimental result of King R. N. [37].
2.4.3 Effect of the Nature of Measuring Matrix on Gas
Wettability
All the above sections use quartz glass slides treated with cationic fluorocar-
bon polymer Zonyl8740 solutions of different concentrations as a measuring
Table 2.14 Contact Angle of Air Bubble and Liquid Drop of n-Octane
C Zonyl8740 wt% θ Air 3 θ Oct 3 γ SW mJ=m 2 γ SV mJ=m 2 A mJ=m 2
0.02 166.36 144.65 2.260 72.33 70.07
0.04 152.48 132.02 4.476 68.413 63.95
0.06 135.84 125.36 3.726 55.45 51.73
0.1 135.52 122.54 4.56 56.00 51.45