Page 307 - Gas Adsorption Equilibria
P. 307
6. Impedance Spectroscopy 293
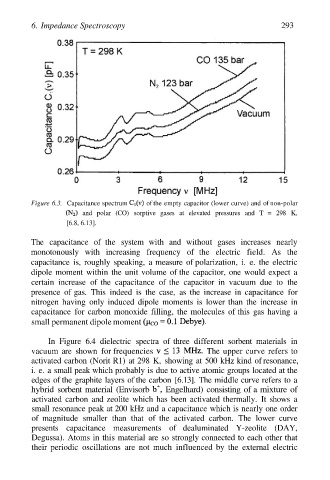
Figure 6.3. Capacitance spectrum of the empty capacitor (lower curve) and of non-polar
and polar (CO) sorptive gases at elevated pressures and T = 298 K,
[6.8, 6.13].
The capacitance of the system with and without gases increases nearly
monotonously with increasing frequency of the electric field. As the
capacitance is, roughly speaking, a measure of polarization, i. e. the electric
dipole moment within the unit volume of the capacitor, one would expect a
certain increase of the capacitance of the capacitor in vacuum due to the
presence of gas. This indeed is the case, as the increase in capacitance for
nitrogen having only induced dipole moments is lower than the increase in
capacitance for carbon monoxide filling, the molecules of this gas having a
small permanent dipole moment
In Figure 6.4 dielectric spectra of three different sorbent materials in
vacuum are shown for frequencies The upper curve refers to
activated carbon (Norit R1) at 298 K, showing at 500 kHz kind of resonance,
i. e. a small peak which probably is due to active atomic groups located at the
edges of the graphite layers of the carbon [6.13]. The middle curve refers to a
hybrid sorbent material (Envisorb Engelhard) consisting of a mixture of
activated carbon and zeolite which has been activated thermally. It shows a
small resonance peak at 200 kHz and a capacitance which is nearly one order
of magnitude smaller than that of the activated carbon. The lower curve
presents capacitance measurements of dealuminated Y-zeolite (DAY,
Degussa). Atoms in this material are so strongly connected to each other that
their periodic oscillations are not much influenced by the external electric