Page 188 - gas transport in porous media
P. 188
182
parameter were presented. Asymptotic solutions for large heating were also available
to support the numerical work. Khanafer and Vafai
Lesnic et al. (1995) presented a detailed analysis of the conjugate free convec-
tion from a horizontal flat plate of finite length embedded in a porous medium. The
boundary-layer approximation was considered in this study. The problem was reduced
to a pair of coupled parabolic partial differential equations for the temperature and
the stream function and full numerical and asymptotic solutions were obtained for
a wide range of coordinate values along the plate. The results for the temperature and
velocity profiles on the plate and in the convective fluid were presented. A compar-
ison between the finite-difference solution and the small and large series expansion
solutions illustrated that the full numerical solution is accurate.
The effect of inertia on free convection from a horizontal surface embedded in
a porous medium was considered by Rees (1996). In this investigation, the author
considered the case where the inertia effects were sufficiently large that the leading-
order boundary layer theory is modified; this was equivalent to reconsidering flow
sufficiently near the leading edge that the induced velocities were large enough for
inertiaeffectstoarise, butsufficientlyfarfromtheleadingedgethattheboundarylayer
approximation remained valid. The resulting nonsimilar boundary layer equations
were solved using the Keller box method. Near the leading edge inertial effects were
found to dominate, but Darcy flow was re-established further downstream.
The free convection in a porous medium adjacent to a horizontal surface subject to
spatial wall temperature distribution was analyzed by Lesnic and Pop (1998). In the
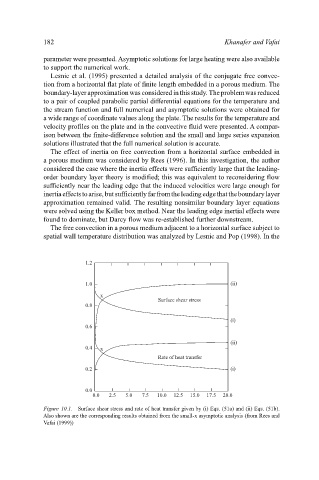
1.2
1.0 (ii)
x
Surface shear stress
0.8
(i)
0.6
(ii)
0.4 x
Rate of heat transfer
0.2 (i)
0.0
0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0
Figure 10.1. Surface shear stress and rate of heat transfer given by (i) Eqs. (51a) and (ii) Eqs. (51b).
Also shown are the corresponding results obtained from the small-x asymptotic analysis (from Rees and
Vafai (1999))