Page 192 - gas transport in porous media
P. 192
Khanafer and Vafai
186
Jian et al. (2001) analyzed numerically natural convection flow from a vertical
flat plate with a surface temperature oscillation. Prandtl number was assumed to be
unity. In the steady case, numerical results for the Grashof numbers 0–625 were
obtained using an iterative approach and the results for small Grashof numbers were
validated using a perturbation method. For larger values of the Grashof numbers, an
unsteady numerical scheme was constructed and the results obtained at large times
were compared with steady state solutions.
10.4 NATURAL CONVECTION FROM AN INCLINED SURFACE
A number of analytical and numerical studies on the natural convection flow along
an inclined surface embedded in a saturated porous medium have been carried out
by a number of investigators due to its applications in geothermal energy, insulation
systems, and heat storage in aquifers. Jang and Chang (1988) have analyzed the free
convection boundary layer flow over an inclined surface embedded in a saturated
porous medium retaining both the streamwise and normal components of the buoy-
ancy force in the momentum equation. The analysis was valid for the wide range of
inclination of the surface ranging from zero to close to 90 degrees from the horizontal.
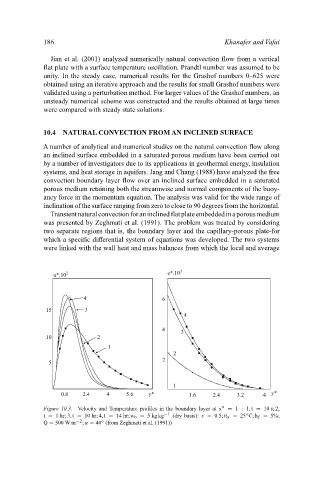
Transientnaturalconvectionforaninclinedflatplateembeddedinaporousmedium
was presented by Zeghmati et al. (1991). The problem was treated by considering
two separate regions that is, the boundary layer and the capillary-porous plate-for
which a specific differential system of equations was developed. The two systems
were linked with the wall heat and mass balances from which the local and average
u*.10 2 e*.10 3
4 6
15 3
4
4
3
10 2
1
2
2
5
1
0.8 2.4 4 5.6 y* 1.6 2.4 3.2 4 y*
Figure 10.3. Velocity and Temperature profiles in the boundary layer at x ∗ = 1:1, t = 10 s; 2,
◦
t = 1 hr; 3, t = 10 hr; 4, t = 14 hr; w o = 5kg kg −1 (dry basis): ε = 0.5; θ α = 25 C; h f = 5%;
◦
Q = 500 W m −2 ; α = 40 (from Zeghmati et al. (1991))