Page 196 - gas transport in porous media
P. 196
190
1.0
M = 0 0.8 Khanafer and Vafai
0.8
1 M = 0
5 0.6 1
0.6 10 5
Γ (j ,0) Γ/υ (j ,0) 10
0.4 Da = 1
Da = 1 0.4
Ec = 0 Ec = 0 Γ = 1
0.2 f = 0.5 Γ = 1 f = 0.5 Ω = 0
Ω = 0 P = 0.7
= 0.7 r
P r
0.0 0.2
0.0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6 0.0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6
j j
(a) (b)
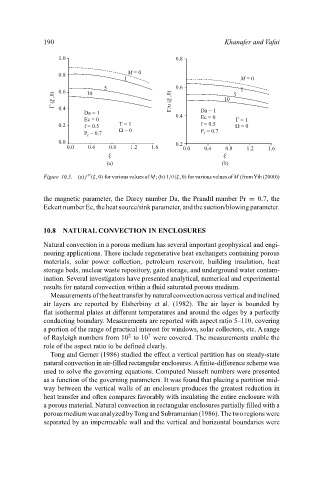
Figure 10.5. (a) f (ξ,0) for various values of M; (b) 1/θ(ξ,0) for various values of M (fromYih (2000))
the magnetic parameter, the Darcy number Da, the Prandtl number Pr = 0.7, the
Eckert number Ec, the heat source/sink parameter, and the suction/blowing parameter.
10.8 NATURAL CONVECTION IN ENCLOSURES
Natural convection in a porous medium has several important geophysical and engi-
neering applications. These include regenerative heat exchangers containing porous
materials, solar power collection, petroleum reservoir, building insulation, heat
storage beds, nuclear waste repository, gain storage, and underground water contam-
ination. Several investigators have presented analytical, numerical and experimental
results for natural convection within a fluid saturated porous medium.
Measurements of the heat transfer by natural convection across vertical and inclined
air layers are reported by Elsherbiny et al. (1982). The air layer is bounded by
flat isothermal plates at different temperatures and around the edges by a perfectly
conducting boundary. Measurements are reported with aspect ratio 5–110, covering
a portion of the range of practical interest for windows, solar collectors, etc. A range
7
2
of Rayleigh numbers from 10 to 10 were covered. The measurements enable the
role of the aspect ratio to be defined clearly.
Tong and Gerner (1986) studied the effect a vertical partition has on steady-state
natural convection in air-filled rectangular enclosures.Afinite-difference scheme was
used to solve the governing equations. Computed Nusselt numbers were presented
as a function of the governing parameters. It was found that placing a partition mid-
way between the vertical walls of an enclosure produces the greatest reduction in
heat transfer and often compares favorably with insulating the entire enclosure with
a porous material. Natural convection in rectangular enclosures partially filled with a
porous medium was analyzed byTong and Subramanian (1986). The two regions were
separated by an impermeable wall and the vertical and horizontal boundaries were