Page 198 - gas transport in porous media
P. 198
Khanafer and Vafai
192
ρ
ρ
< v > at t 1 < v > at t 4
γ
γ
g
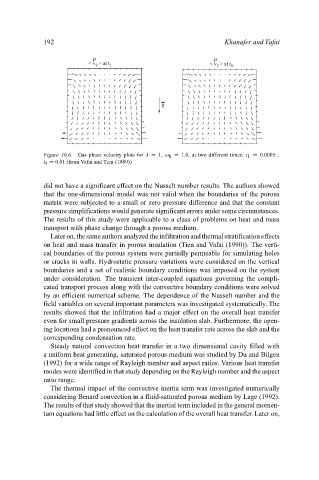
Figure 10.6. Gas phase velocity plots for A = 1, ω h = 1.0, at two different times: t 1 = 0.0005 :
t 4 = 0.01 (from Vafai and Tien (1989))
did not have a significant effect on the Nusselt number results. The authors showed
that the one-dimensional model was not valid when the boundaries of the porous
matrix were subjected to a small or zero pressure difference and that the constant
pressure simplifications would generate significant errors under some circumstances.
The results of this study were applicable to a class of problems on heat and mass
transport with phase change through a porous medium.
Later on, the same authors analyzed the infiltration and thermal stratification effects
on heat and mass transfer in porous insulation (Tien and Vafai (1990)). The verti-
cal boundaries of the porous system were partially permeable for simulating holes
or cracks in walls. Hydrostatic pressure variations were considered on the vertical
boundaries and a set of realistic boundary conditions was imposed on the system
under consideration. The transient inter-coupled equations governing the compli-
cated transport process along with the convective boundary conditions were solved
by an efficient numerical scheme. The dependence of the Nusselt number and the
field variables on several important parameters was investigated systematically. The
results showed that the infiltration had a major effect on the overall heat transfer
even for small pressure gradients across the insulation slab. Furthermore, the open-
ing locations had a pronounced effect on the heat transfer rate across the slab and the
corresponding condensation rate.
Steady natural convection heat transfer in a two dimensional cavity filled with
a uniform heat generating, saturated porous medium was studied by Du and Bilgen
(1992) for a wide range of Rayleigh number and aspect ratios. Various heat transfer
modes were identified in that study depending on the Rayleigh number and the aspect
ratio range.
The thermal impact of the convective inertia term was investigated numerically
considering Benard convection in a fluid-saturated porous medium by Lage (1992).
The results of that study showed that the inertial term included in the general momen-
tum equations had little effect on the calculation of the overall heat transfer. Later on,