Page 194 - gas transport in porous media
P. 194
188
4.0
Local non-smilarity solutions Khanafer and Vafai
Local smilarity solutions
3.0
λ
0
q c q p 1/4
1/3
1/2
3/4
2.0 1
1.0
0 2 4 6 8 10
j
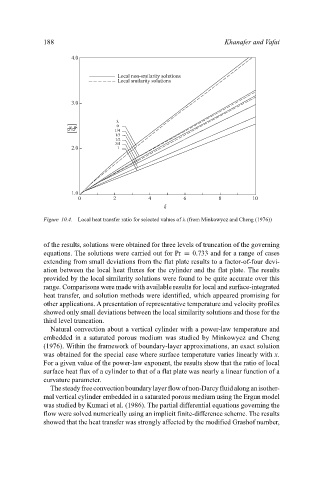
Figure 10.4. Local heat transfer ratio for selected values of λ (from Minkowycz and Cheng (1976))
of the results, solutions were obtained for three levels of truncation of the governing
equations. The solutions were carried out for Pr = 0.733 and for a range of cases
extending from small deviations from the flat plate results to a factor-of-four devi-
ation between the local heat fluxes for the cylinder and the flat plate. The results
provided by the local similarity solutions were found to be quite accurate over this
range. Comparisons were made with available results for local and surface-integrated
heat transfer, and solution methods were identified, which appeared promising for
other applications. A presentation of representative temperature and velocity profiles
showed only small deviations between the local similarity solutions and those for the
third level truncation.
Natural convection about a vertical cylinder with a power-law temperature and
embedded in a saturated porous medium was studied by Minkowycz and Cheng
(1976). Within the framework of boundary-layer approximations, an exact solution
was obtained for the special case where surface temperature varies linearly with x.
For a given value of the power-law exponent, the results show that the ratio of local
surface heat flux of a cylinder to that of a flat plate was nearly a linear function of a
curvature parameter.
Thesteadyfreeconvectionboundarylayerflowofnon-Darcyfluidalonganisother-
mal vertical cylinder embedded in a saturated porous medium using the Ergun model
was studied by Kumari et al. (1986). The partial differential equations governing the
flow were solved numerically using an implicit finite-difference scheme. The results
showed that the heat transfer was strongly affected by the modified Grashof number,