Page 252 - Geochemical Remote Sensing of The Sub-Surface
P. 252
Gas geochemistry surveys for petroleum 225
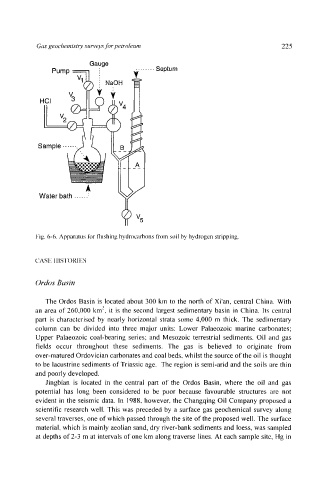
Gauge
........ Septum
Pump ~ w
Vl(~ NaOH
V 3 I'T" ~ ~ II
HCi v4
V2
Sample ......
H-F-
Water bath '
i:ig. 6-6. Apparatus lbr flushing hydrocarbons t'ronl soil by hydrogen stripping.
CASI'~ ! IIS'I'()RIES
Ordos Basin
Tile Ordos Basin is located about 300 km to the north of Xi'an, central China. With
an area of 260,000 km 2, it is the second largest sedimentary basin in China. Its central
part is characterised by nearly horizontal strata some 4,000 m thick. The sedimentary
column can be divided into three major units: Lower Palaeozoic marine carbonates:
Upper Palaeozoic coal-bearing series: and Mesozoic terrestrial sediments. Oil and gas
fields occur throughout these sediments. The gas is believed to originate from
over-matured Ordovician carbonates and coal beds, whilst the source of the oil is thought
to be lacustrine sediments of Triassic age. The region is semi-arid and the soils are thin
and poorly developed.
Jingbian is located in the central part of the Ordos Basin, where the oil and gas
potential has long been considered to be poor because favourable structures are not
evident in the seismic data. In 1988, however, the Changqing Oil Company proposed a
scientific research well. This was preceded by a surface gas geochemical survey along
several traverses, one of which passed through the site of the proposed well. The surface
material, which is mainly aeolian sand, dry river-bank sediments and loess, was sampled
at depths of 2-3 m at intervals of one km along traverse lines. At each sample site, Hg in