Page 209 - Geochemistry of Oil Field Waters
P. 209
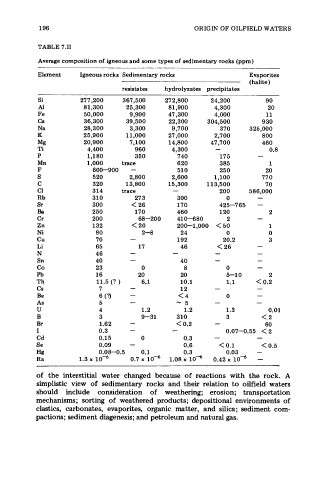
196 ORIGIN OF OILFIELD WATERS
TABLE 7.11
Average composition of igneous and some types of sedimentary rocks (ppm)
Element Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Evaporites
(halite)
resistates hydrolyzates precipitates
Si 277,200 367,500 272,800 24,200 90
A1 81,300 25,300 81,900 4,300 20
Fe 50,000 9,900 47,300 4,000 11
Ca 36,300 39,500 22,300 304,500 930
Na 28,300 3,300 9,700 370 325,000
K 25,900 11,000 27,000 2,700 800
Mg 20,900 7,100 14,800 47,700 460
Ti 4,400 960 4,300 - 0.8
P 1,180 350 740 175 -
Mn 1,000 trace 620 385 1
F 600-900 - 510 250 20
S 520 2,800 2,600 1,100 770
C 320 13,800 15,300 113,500 70
c1 314 trace - 200 586,000
Rb 310 27 3 300 0 -
Sr 300 < 26 170 425-765 -
Ba 250 170 460 120 2
Cr 200 68-200 410-680 2 -
Zn 132 < 20 200-1,000 < 50 1
Ni 80 2-8 24 0 0
cu 70 - 192 20.2 3
Li 65 17 46 < 26 -
N 46 - - - -
Sn 40 - 40 - -
co 23 0 8 0 -
Pb 16 20 20 5-1 0 2
Th 11.5 (? ) 6.1 10.1 1.1 < 0.2
cs 7 - 12 - -
Be 6 (3 - <4 0 -
As 5 - -5 - -
U 4 1.2 1.2 1.3 0.01
B 3 9-31 310 3 <2
Br 1.62 - < 0.2 - 60
I 0.3 - - 0.07-0.55 < 2
Cd 0.15 0 0.3 - -
Se 0.09 - 0.6 < 0.1 < 0.5
Hg 0.08-0.5 0.1 0.3 0.03 -
Ra 1.3 x 0.7 x 1.08 x lod 0.42 x lod -
of the interstitial water changed because of reactions with the rock. A
simplistic view of sedimentary rocks and their relation to oilfield waters
should include consideration of weathering; erosion; transportation
mechanisms; sorting of weathered products; depositional environments of
clastics, carbonates, evaporites, organic matter, and silica; sediment com-
pactions; sediment diagenesis; and petroleum and natural gas.