Page 212 - Geochemistry of Oil Field Waters
P. 212
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 199
becomes more concentrated with certain dissolved solids, the pH can be
more stable because of buffer effects.
A solution containing an activity of orthosilicic acid greater than its solu-
bility product (K ) is oversaturated and SiOz will precipitate. If the activity
s.p
of orthosilicic acid is less than its Ksp, SiQz can dissolve until (H4Si0,)
= Ksp. The same applies for other constituents.
Complex compounds and ion pairs are important chemical transport
mechanisms. An example of a complex compound is a metal chelate such as
copper chelated with ethylenediamine tetraacetate, with the interacting
ligands immediately adjacent to the metal cation. An ion pair is formed if
the coordinated water is retained in forming the complex (Stumm and
Morgan, 1970).
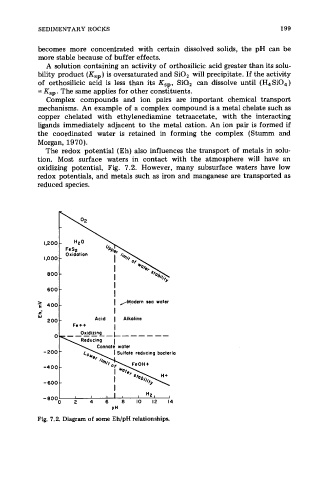
The redox potential (Eh) also influences the transport of metals in solu-
tion. Most surface waters in contact with the atmosphere will have an
oxidizing potential, Fig. 7.2. However, many subsurface waters have low
redox potentials, and metals such as iron and manganese are transported as
reduced species.
600 - I
I /M,odern sea water
400-
r I
200 - Acid I Alkaline
W
Fe++ I
-400 -
-600 -
I I I I I H2, I
-eooo 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
PH
Fig. 7.2. Diagram of some EhlpH relationships.