Page 198 - Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs
P. 198
FRACTURES AND FRACTURED RESERVOIRS 179
σ
1
A σ
C 2
B
σ σ
3 3
σ
2
σ
1
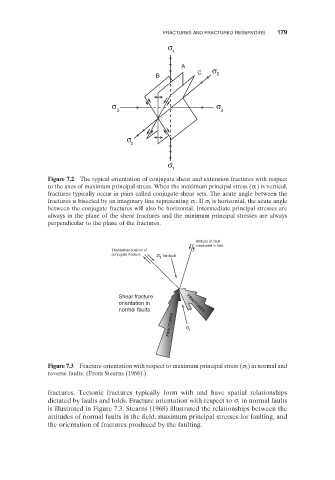
Figure 7.2 The typical orientation of conjugate shear and extension fractures with respect
) is vertical,
to the axes of maximum principal stress. When the maximum principal stress ( σ 1
fractures typically occur in pairs called conjugate shear sets. The acute angle between the
is horizontal, the acute angle
fractures is bisected by an imaginary line representing σ 1 . If σ 1
between the conjugate fractures will also be horizontal. Intermediate principal stresses are
always in the plane of the shear fractures and the minimum principal stresses are always
perpendicular to the plane of the fractures.
Attitude of fault
measured in field
Theoretical position of
conjugate fracture
σ for fault
1
Shear fracture
orientation in FRACTURES
normal faults
FRACTURES σ 1
) in normal and
Figure 7.3 Fracture orientation with respect to maximum principal stress ( σ 1
reverse faults. (From Stearns (1968) .)
fractures. Tectonic fractures typically form with and have spatial relationships
in normal faults
dictated by faults and folds. Fracture orientation with respect to σ 1
is illustrated in Figure 7.3 . Stearns (1968) illustrated the relationships between the
attitudes of normal faults in the field, maximum principal stresses for faulting, and
the orientation of fractures produced by the faulting.