Page 26 - Geometric Modeling and Algebraic Geometry
P. 26
20 T. Dokken
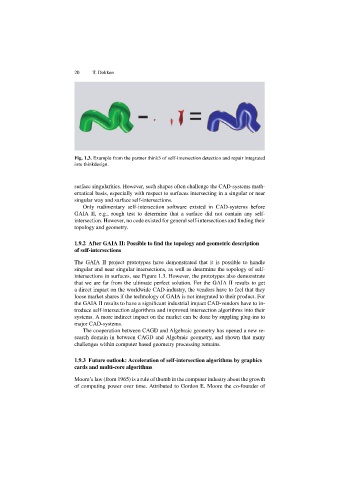
Fig. 1.3. Example from the partner think3 of self-intersection detection and repair integrated
into thinkdesign.
surface singularities. However, such shapes often challenge the CAD-systems math-
ematical basis, especially with respect to surfaces intersecting in a singular or near
singular way and surface self-intersections.
Only rudimentary self-intersection software existed in CAD-systems before
GAIA II, e.g., rough test to determine that a surface did not contain any self-
intersection. However, no code existed for general self-intersections and finding their
topology and geometry.
1.9.2 After GAIA II: Possible to find the topology and geometric description
of self-intersections
The GAIA II project prototypes have demonstrated that it is possible to handle
singular and near singular intersections, as well as determine the topology of self-
intersections in surfaces, see Figure 1.3. However, the prototypes also demonstrate
that we are far from the ultimate perfect solution. For the GAIA II results to get
a direct impact on the worldwide CAD-industry, the vendors have to feel that they
loose market shares if the technology of GAIA is not integrated to their product. For
the GAIA II results to have a significant industrial impact CAD-vendors have to in-
troduce self-intersection algorithms and improved intersection algorithms into their
systems. A more indirect impact on the market can be done by suppling plug-ins to
major CAD-systems.
The cooperation between CAGD and Algebraic geometry has opened a new re-
search domain in between CAGD and Algebraic geometry, and shown that many
challenges within computer based geometry processing remains.
1.9.3 Future outlook: Acceleration of self-intersection algorithms by graphics
cards and multi-core algorithms
Moore’s law (from 1965) is a rule of thumb in the computer industry about the growth
of computing power over time. Attributed to Gordon E. Moore the co-founder of