Page 42 - Geothermal Energy Renewable Energy and The Environment
P. 42
Sources of Geothermal Heat: Earth as a Heat Engine 25
–30 –15 0 15 30 45 Heat flow
2
(mW/m )
Iceland > 150
IS
80 – 150
50 – 80
30 – 50
FI
< 30
60
NO RU
SE
EE
LV
Soultz-sous- DK
forets LT
IE
GB BY
NL
BE PL
DE
LU
CZ UA
SK
45 MD
FR CH AT HU
SI RO
HR
IT
BA
YU
BG
MK
PT ES AL
GR TR
Larderello
Aydin
Denizli
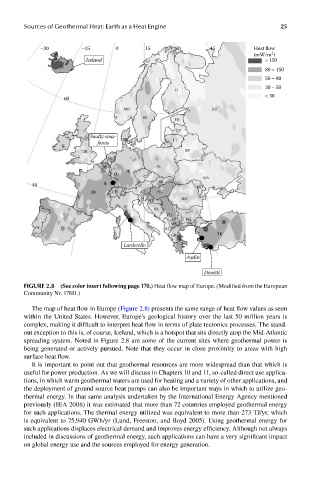
FIGUre 2.8 (See color insert following page 17.0..) Heat flow map of Europe. (Modified from the European
Community Nr. 17811.)
The map of heat flow in Europe (Figure 2.8) presents the same range of heat flow values as seen
within the United States. However, Europe’s geological history over the last 50 million years is
complex, making it difficult to interpret heat flow in terms of plate tectonics processes. The stand-
out exception to this is, of course, Iceland, which is a hotspot that sits directly atop the Mid-Atlantic
spreading system. Noted in Figure 2.8 are some of the current sites where geothermal power is
being generated or actively pursued. Note that they occur in close proximity to areas with high
surface heat flow.
It is important to point out that geothermal resources are more widespread than that which is
useful for power production. As we will discuss in Chapters 10 and 11, so-called direct use applica-
tions, in which warm geothermal waters are used for heating and a variety of other applications, and
the deployment of ground source heat pumps can also be important ways in which to utilize geo-
thermal energy. In that same analysis undertaken by the International Energy Agency mentioned
previously (IEA 2006) it was estimated that more than 72 countries employed geothermal energy
for such applications. The thermal energy utilized was equivalent to more than 273 TJ/yr, which
is equivalent to 75,940 GWh/yr (Lund, Freeston, and Boyd 2005). Using geothermal energy for
such applications displaces electrical demand and improves energy efficiency. Although not always
included in discussions of geothermal energy, such applications can have a very significant impact
on global energy use and the sources employed for energy generation.