Page 149 - Global Project Management Handbook
P. 149
RISK IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT 6-17
Walewski J, Gibson G, Jackson Y, Vines E. 2004. Risk assessment on international projects: a
management approach, in Proceedings of 2004 PMI Research Conference, July 2004, London.
Walewski J. 2005. International project risk assessment. Doctoral dissertation, University of
Texas at Austin.
APPENDIX 6A
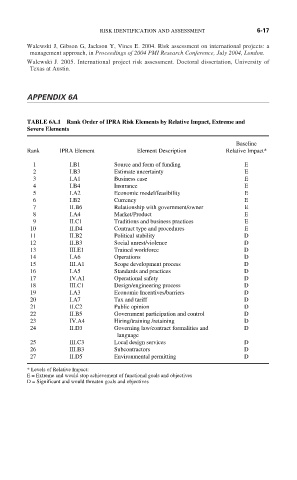
TABLE 6A.1 Rank Order of IPRA Risk Elements by Relative Impact, Extreme and
Severe Elements
Baseline
Rank IPRA Element Element Description Relative Impact*
1 I.B1 Source and form of funding E
2 I.B3 Estimate uncertainty E
3 I.A1 Business case E
4 I.B4 Insurance E
5 I.A2 Economic model/feasibility E
6 I.B2 Currency E
7 II.B6 Relationship with government/owner E
8 I.A4 Market/Product E
9 II.C1 Traditions and business practices E
10 II.D4 Contract type and procedures E
11 II.B2 Political stability D
12 II.B3 Social unrest/violence D
13 III.E1 Trained workforce D
14 I.A6 Operations D
15 III.A1 Scope development process D
16 I.A5 Standards and practices D
17 IV.A1 Operational safety D
18 III.C1 Design/engineering process D
19 I.A3 Economic Incentives/barriers D
20 I.A7 Tax and tariff D
21 II.C2 Public opinion D
22 II.B5 Government participation and control D
23 IV.A4 Hiring/training /retaining D
24 II.D3 Governing law/contract formalities and D
language
25 III.C3 Local design services D
26 III.B3 Subcontractors D
27 II.D5 Environmental permitting D
* Levels of Relative Impact:
E = Extreme and would stop achievement of functional goals and objectives
D = Significant and would threaten goals and objectives