Page 298 - Global Tectonics
P. 298
SUBDUCTION ZONES 283
180 W 175 W
Samoa
15 S
400 1 00
300
Fiji Is. 200
N
ETZ
CLSC
Lau
ELSC 20 S
basin
ridge T
Lau ridge VFR Tonga Tonga trench
AUSTRALIAN PACIFIC
PLATE PLATE
25 S
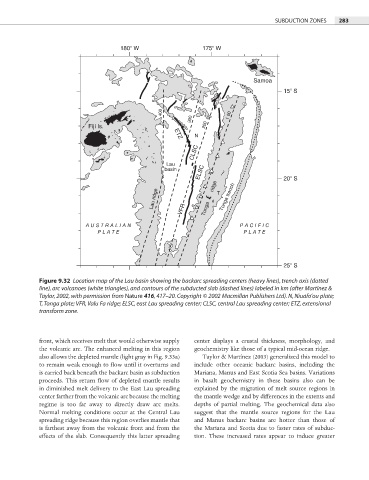
Figure 9.32 Location map of the Lau basin showing the backarc spreading centers (heavy lines), trench axis (dotted
line), arc volcanoes (white triangles), and contours of the subducted slab (dashed lines) labeled in km (after Martínez &
Taylor, 2002, with permission from Nature 416, 417–20. Copyright © 2002 Macmillan Publishers Ltd). N, Niuafo’ou plate;
T, Tonga plate; VFR, Valu Fa ridge; ELSC, east Lau spreading center; CLSC, central Lau spreading center; ETZ, extensional
transform zone.
front, which receives melt that would otherwise supply center displays a crustal thickness, morphology, and
the volcanic arc. The enhanced melting in this region geochemistry like those of a typical mid-ocean ridge.
also allows the depleted mantle (light gray in Fig. 9.33a) Taylor & Martínez (2003) generalized this model to
to remain weak enough to flow until it overturns and include other oceanic backarc basins, including the
is carried back beneath the backarc basin as subduction Mariana, Manus and East Scotia Sea basins. Variations
proceeds. This return flow of depleted mantle results in basalt geochemistry in these basins also can be
in diminished melt delivery to the East Lau spreading explained by the migration of melt source regions in
center farther from the volcanic arc because the melting the mantle wedge and by differences in the extents and
regime is too far away to directly draw arc melts. depths of partial melting. The geochemical data also
Normal melting conditions occur at the Central Lau suggest that the mantle source regions for the Lau
spreading ridge because this region overlies mantle that and Manus backarc basins are hotter than those of
is farthest away from the volcanic front and from the the Mariana and Scotia due to faster rates of subduc-
effects of the slab. Consequently this latter spreading tion. These increased rates appear to induce greater