Page 149 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 149
Section 9.0 - Durability Aspects 133
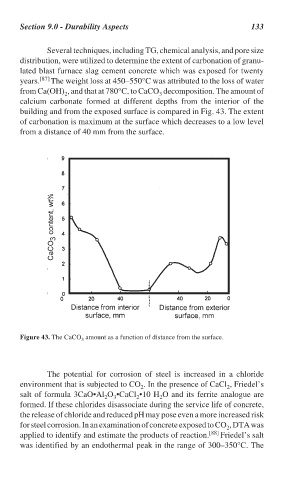
Several techniques, including TG, chemical analysis, and pore size
distribution, were utilized to determine the extent of carbonation of granu-
lated blast furnace slag cement concrete which was exposed for twenty
years. [87] The weight loss at 450–550°C was attributed to the loss of water
from Ca(OH) , and that at 780°C, to CaCO decomposition. The amount of
3
2
calcium carbonate formed at different depths from the interior of the
building and from the exposed surface is compared in Fig. 43. The extent
of carbonation is maximum at the surface which decreases to a low level
from a distance of 40 mm from the surface.
Figure 43. The CaCO amount as a function of distance from the surface.
3
The potential for corrosion of steel is increased in a chloride
environment that is subjected to CO . In the presence of CaCl , Friedel’s
2 2
salt of formula 3CaO•Al O •CaCl •10 H O and its ferrite analogue are
2
3
2
2
formed. If these chlorides disassociate during the service life of concrete,
the release of chloride and reduced pH may pose even a more increased risk
for steel corrosion. In an examination of concrete exposed to CO , DTA was
2
applied to identify and estimate the products of reaction. [88] Friedel’s salt
was identified by an endothermal peak in the range of 300–350°C. The