Page 213 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 213
Section 2.0 - Calcium Chloride 197
without the chloride. [10] This would imply that a higher C/S ratio C-S-H
product results in the presence of calcium chloride. There is also evidence
that in the hydration of C S some chloride is bound rigidly.
2
The reaction of C A with calcium chloride results in the formation
3
of high and low forms of tricalcium chloroaluminates. Under normal
conditions of hydration, the low form, viz., C A•CaCl •XH O is obtained.
3 2 2
The DTA technique may be used to differentiate between the two forms.
Endothermal effects at about 190 and 350°C are caused by the low form and
the endotherm at about 160°C is exhibited by the high form. In the system
C A-CaO-CaCl -H O, at higher concentrations of calcium chloride, cal-
2
2
3
cium hydroxychloride is formed that is identified by peaks at 130, 145, and
485°C. [11]
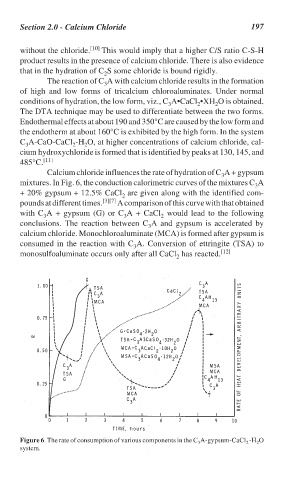
Calcium chloride influences the rate of hydration of C A + gypsum
3
mixtures. In Fig. 6, the conduction calorimetric curves of the mixtures C A
3
+ 20% gypsum + 12.5% CaCl are given along with the identified com-
2
pounds at different times. [3][7] A comparison of this curve with that obtained
with C A + gypsum (G) or C A + CaCl would lead to the following
3
3
2
conclusions. The reaction between C A and gypsum is accelerated by
3
calcium chloride. Monochloroaluminate (MCA) is formed after gypsum is
consumed in the reaction with C A. Conversion of ettringite (TSA) to
3
monosulfoaluminate occurs only after all CaCl has reacted. [12]
2
Figure 6. The rate of consumption of various components in the C A-gypsum-CaCl -H O
2
2
3
system.