Page 326 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 326
Section 3.0 - Silica Fume 303
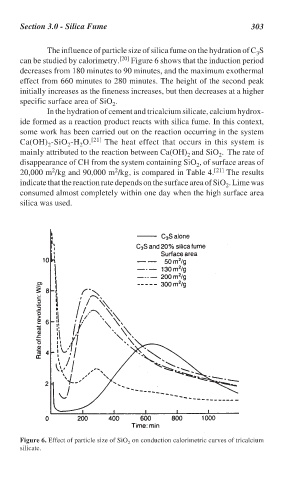
The influence of particle size of silica fume on the hydration of C S
3
can be studied by calorimetry. [20] Figure 6 shows that the induction period
decreases from 180 minutes to 90 minutes, and the maximum exothermal
effect from 660 minutes to 280 minutes. The height of the second peak
initially increases as the fineness increases, but then decreases at a higher
specific surface area of SiO .
2
In the hydration of cement and tricalcium silicate, calcium hydrox-
ide formed as a reaction product reacts with silica fume. In this context,
some work has been carried out on the reaction occurring in the system
Ca(OH) -SiO -H O. [21] The heat effect that occurs in this system is
2
2
2
mainly attributed to the reaction between Ca(OH) and SiO . The rate of
2
2
disappearance of CH from the system containing SiO , of surface areas of
2
2
2
20,000 m /kg and 90,000 m /kg, is compared in Table 4. [21] The results
indicate that the reaction rate depends on the surface area of SiO . Lime was
2
consumed almost completely within one day when the high surface area
silica was used.
Figure 6. Effect of particle size of SiO on conduction calorimetric curves of tricalcium
2
silicate.