Page 37 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 37
Section 3.0 - Modern Techniques 21
is measured as a function of time or temperature. The plot of expansion (or
contraction) versus temperature (or time) can then be used to obtain T , the
g
coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), softening temperature, and Young’s
modulus.
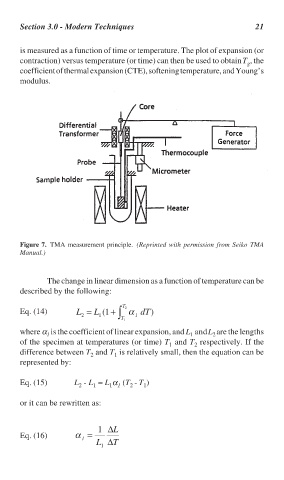
Figure 7. TMA measurement principle. (Reprinted with permission from Seiko TMA
Manual.)
The change in linear dimension as a function of temperature can be
described by the following:
(
Eq. (14) L = L 1+ ∫ T 2 α dT)
2 1 l
T 1
where α is the coefficient of linear expansion, and L and L are the lengths
2
1
l
of the specimen at temperatures (or time) T and T respectively. If the
2
1
difference between T and T is relatively small, then the equation can be
2 1
represented by:
Eq. (15) L - L = L α (T - T )
1 1
2 1
1
2
or it can be rewritten as:
1 ∆ L
Eq. (16) α =
L ∆ T
l
1