Page 513 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 513
Section 9.0 - Industrial Applications 485
-1 [23]
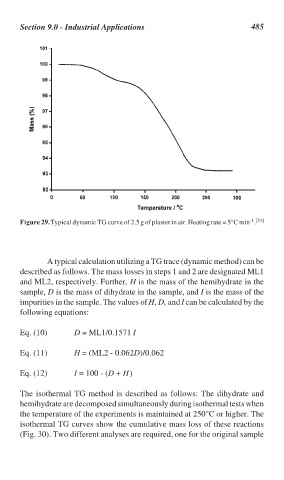
Figure 29. Typical dynamic TG curve of 2.5 g of plaster in air. Heating rate = 5°C min .
A typical calculation utilizing a TG trace (dynamic method) can be
described as follows. The mass losses in steps 1 and 2 are designated ML1
and ML2, respectively. Further, H is the mass of the hemihydrate in the
sample, D is the mass of dihydrate in the sample, and I is the mass of the
impurities in the sample. The values of H, D, and I can be calculated by the
following equations:
Eq. (10) D = ML1/0.1571 I
Eq. (11) H = (ML2 - 0.062D)/0.062
Eq. (12) I = 100 - (D + H)
The isothermal TG method is described as follows: The dihydrate and
hemihydrate are decomposed simultaneously during isothermal tests when
the temperature of the experiments is maintained at 250°C or higher. The
isothermal TG curves show the cumulative mass loss of these reactions
(Fig. 30). Two different analyses are required, one for the original sample