Page 303 - Geology and Geochemistry of Oil and Gas
P. 303
264 MATHEMATICAL MODELING IN PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
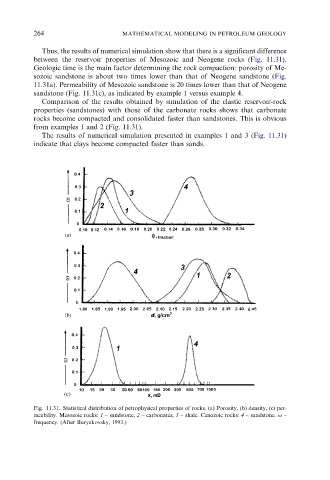
Thus, the results of numerical simulation show that there is a significant difference
between the reservoir properties of Mesozoic and Neogene rocks (Fig. 11.31).
Geologic time is the main factor determining the rock compaction: porosity of Me-
sozoic sandstone is about two times lower than that of Neogene sandstone (Fig.
11.31a). Permeability of Mesozoic sandstone is 20 times lower than that of Neogene
sandstone (Fig. 11.31c), as indicated by example 1 versus example 4.
Comparison of the results obtained by simulation of the clastic reservoir-rock
properties (sandstones) with those of the carbonate rocks shows that carbonate
rocks become compacted and consolidated faster than sandstones. This is obvious
from examples 1 and 2 (Fig. 11.31).
The results of numerical simulation presented in examples 1 and 3 (Fig. 11.31)
indicate that clays become compacted faster than sands.
Fig. 11.31. Statistical distribution of petrophysical properties of rocks. (a) Porosity, (b) density, (c) per-
meability. Mesozoic rocks: 1 – sandstone, 2 – carbonates, 3 – shale. Cenozoic rocks: 4 – sandstone. o –
frequency. (After Buryakovsky, 1993.)