Page 458 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 458
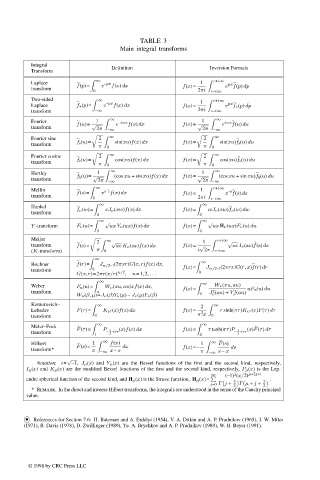
TABLE 3
Main integral transforms
Integral Definition Inversion Formula
Transform
Laplace f(p)= ∞ e –px f(x) dx 1 c+i∞ px
transform 0 f(x)= 2πi c–i∞ e f(p) dp
Two-sided ∞ 1 c+i∞
Laplace f ∗(p)= e –px f(x) dx f(x)= e px
f ∗(p) dp
transform –∞ 2πi c–i∞
Fourier 1 ∞ –iux 1 ∞
f(u) du
f(u)= √ e f(x) dx f(x)= √ e iux
transform 2π –∞ 2π –∞
Fourier sine 2 ∞ 2 ∞
transform f s(u)= π 0 sin(xu)f(x) dx f(x)= π 0 sin(xu)f s(u) du
Fourier cosine 2 ∞ 2 ∞
f c(u)= cos(xu)f(x) dx f(x)= cos(xu)f c(u) du
transform π 0 π 0
Hartley 1 ∞ (cos xu + sin xu)f(x) dx 1 ∞ (cos xu + sin xu)f h (u) du
transform f h (u)= √ 2π –∞ f(x)= √ 2π –∞
Mellin ∞ s–1 1 c+i∞ –s
transform f(s)= x f(x) dx f(x)= 2πi x f(s) ds
0 c–i∞
Hankel f ν(w)= ∞ xJ ν(xw)f(x) dx f(x)= ∞ wJ ν(xw)f ν(w) dw
transform 0 0
∞ √ ∞ √
Y -transform F ν(u)= ux Y ν(ux)f(x) dx f(x)= ux H ν(ux)F ν(u) du
0 0
Meijer
2 ∞ √ 1 c+i∞ √
transform f(s)= sxK ν(sx)f(x) dx f(x)= √ sxI ν(sx)f(s) ds
(K-transform) π 0 i 2π c–i∞
∞
Bochner f(r)= J n/2–1 (2πxr)G(x, r)f(x) dx, ∞
transform 0 f(x)= J n/2–1 (2πrx)G(r, x)f(r) dr
G(x, r)=2πr(x/r) n/2 , n=1, 2, ... 0
∞
Weber F a(u)= W ν(xu, au)xf(x) dx, f(x)= ∞ W ν(xu, au) uF a(u) du
transform a J ν (au)+ Y ν (au)
2
2
W ν(β, µ)≡J ν(β)Y ν(µ) – J ν(µ)Y ν(β) 0
Kontorovich– ∞ 2 ∞
Lebedev F(τ)= K iτ (x)f(x) dx f(x)= 2 τ sinh(πτ)K iτ (x)F(τ) dτ
transform 0 π x 0
Meler–Fock F(τ)= ∞ (x)f(x) dx f(x)= ∞ (x)F(τ) dτ
– +iτ
transform 1 P 1 2 0 τ tanh(πτ)P 1 2
– +iτ
F(s)
Hilbert F(s)= 1 ∞ f(x) dx 1 ∞
transform* π –∞ x – s f(x)=– π –∞ s – x ds
√
Notation: i= –1, J µ(x) and Y µ(x) are the Bessel functions of the first and the second kind, respectively,
I µ(x) and K µ(x) are the modified Bessel functions of the first and the second kind, respectively, P µ(x) is the Leg-
j
∞ (–1) (x/2) µ+2j+1
endre spherical function of the second kind, and H µ(x) is the Struve function, H µ(x)=
.
j=0 Γ j + 3 2 Γ µ + j + 3 2
*REMARK. In the direct and inverse Hilbert transforms, the integrals are understood in the sense of the Cauchy principal
value.
•
References for Section 7.6: H. Bateman and A. Erd´ elyi (1954), V. A. Ditkin and A. P. Prudnikov (1965), J. W. Miles
(1971), B. Davis (1978), D. Zwillinger (1989), Yu. A. Brychkov and A. P. Prudnikov (1989), W. H. Beyer (1991).
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 439