Page 257 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 257
256 10. Research methods in flow assurance
macromolecule and the initial position on the crystal surface, and Φ is the angle of the macro-
molecule rotation about its center line relative to the initial position. The macromolecule was
flat, relative to the surface, keeping the sixth variable 0 fixed. The intermolecular energy (po-
tential energy between molecules in current conformation relative to infinitely distant mole-
cules) was monitored during the docking. The conformation with the lowest intermolecular
energy was chosen as the preferred orientation of the macromolecule on the crystal surface.
A typical value of the interaction energy prior to the relaxation of the macromolecule on the
crystal surface was of the order of tens of kilocalories per mole. The energy of the whole sys-
tem was minimized (the macromolecule was relaxed on the crystal surface). The final system
energies are given in Table 10.9.
Data analysis
One run was performed for each polymer chain. For each run the following final values
were inspected:
(a) The number of hydrogen bonds between the macromolecule and water molecules
of the crystal. Hydrogen bonds were defined by the following default values stored
in SYBYLQ two water molecules were found to be hydrogen bonded if the length of
hydrogen bond were less than or equal to 0.285 nm and the HO-----H angle >120%.
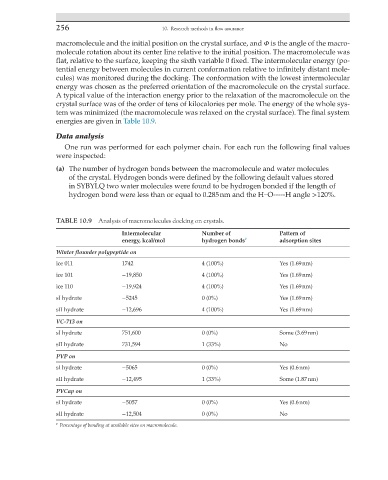
TABLE 10.9 Analysis of macromolecules docking on crystals.
Intermolecular Number of Pattern of
energy, kcal/mol hydrogen bonds a adsorption sites
Winter flounder polypeptide on
ice 011 1742 4 (100%) Yes (1.69 nm)
ice 101 −19,850 4 (100%) Yes (1.69 nm)
ice 110 −19,924 4 (100%) Yes (1.69 nm)
sI hydrate −5245 0 (0%) Yes (1.69 nm)
sII hydrate −12,696 4 (100%) Yes (1.69 nm)
VC-713 on
sI hydrate 751,600 0 (0%) Some (3.69 nm)
sII hydrate 731,594 1 (33%) No
PVP on
sI hydrate −5065 0 (0%) Yes (0.6 nm)
sII hydrate −12,495 1 (33%) Some (1.87 nm)
PVCap on
sI hydrate −5057 0 (0%) Yes (0.6 nm)
sII hydrate −12,504 0 (0%) No
a Percentage of bonding at available sites on macromolecule.