Page 260 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 260
Molecular modeling 259
FIG. 10.25 Conformation of the winter flounder polypeptide docked on sII hydrate. Dashed lines represent hy-
drogen bonds. Winter flounder polypeptide is hydrogen bonded by five carbonyl CO groups to hydrogens of
water molecules in hydrate.
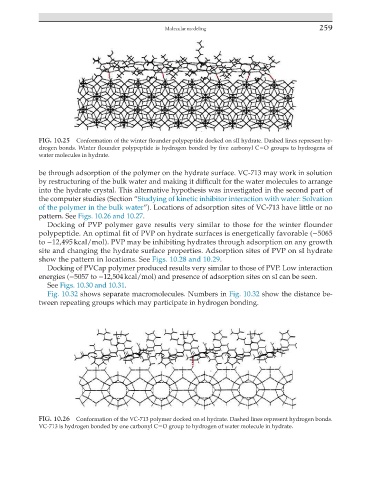
be through adsorption of the polymer on the hydrate surface. VC-713 may work in solution
by restructuring of the bulk water and making it difficult for the water molecules to arrange
into the hydrate crystal. This alternative hypothesis was investigated in the second part of
the computer studies (Section “Studying of kinetic inhibitor interaction with water: Solvation
of the polymer in the bulk water”). Locations of adsorption sites of VC-713 have little or no
pattern. See Figs. 10.26 and 10.27.
Docking of PVP polymer gave results very similar to those for the winter flounder
polypeptide. An optimal fit of PVP on hydrate surfaces is energetically favorable (−5065
to −12,495 kcal/mol). PVP may be inhibiting hydrates through adsorption on any growth
site and changing the hydrate surface properties. Adsorption sites of PVP on sI hydrate
show the pattern in locations. See Figs. 10.28 and 10.29.
Docking of PVCap polymer produced results very similar to those of PVP. Low interaction
energies (−5057 to −12,504 kcal/mol) and presence of adsorption sites on sI can be seen.
See Figs. 10.30 and 10.31.
Fig. 10.32 shows separate macromolecules. Numbers in Fig. 10.32 show the distance be-
tween repeating groups which may participate in hydrogen bonding.
FIG. 10.26 Conformation of the VC-713 polymer docked on sI hydrate. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds.
VC-713 is hydrogen bonded by one carbonyl CO group to hydrogen of water molecule in hydrate.