Page 173 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 173
156 Chapter 4 - Introduction to Concrete Admixtures
2.6 Formates
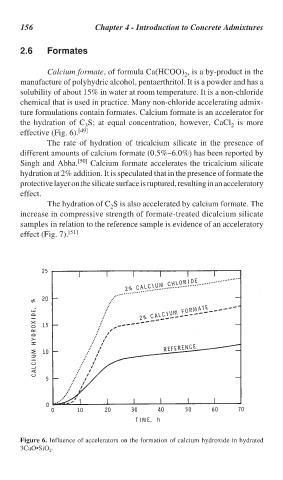
Calcium formate, of formula Ca(HCOO) , is a by-product in the
2
manufacture of polyhydric alcohol, pentaerthritol. It is a powder and has a
solubility of about 15% in water at room temperature. It is a non-chloride
chemical that is used in practice. Many non-chloride accelerating admix-
ture formulations contain formates. Calcium formate is an accelerator for
the hydration of C S; at equal concentration, however, CaCl is more
3 2
effective (Fig. 6). [49]
The rate of hydration of tricalcium silicate in the presence of
different amounts of calcium formate (0.5%–6.0%) has been reported by
Singh and Abha. [50] Calcium formate accelerates the tricalcium silicate
hydration at 2% addition. It is speculated that in the presence of formate the
protective layer on the silicate surface is ruptured, resulting in an acceleratory
effect.
The hydration of C S is also accelerated by calcium formate. The
2
increase in compressive strength of formate-treated dicalcium silicate
samples in relation to the reference sample is evidence of an acceleratory
effect (Fig. 7). [51]
Figure 6. Influence of accelerators on the formation of calcium hydroxide in hydrated
3CaO•SiO .
2