Page 178 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 178
Section 2.0 - Accelerators 161
A new accelerator formulation consisting of inorganic salts and
organic compounds (one of these being a sulfonate dispersant) is claimed
to be effective at a low temperature of -7°C as well at a higher temperature
of 35°C. It accelerates setting, increases early and ultimate strengths,
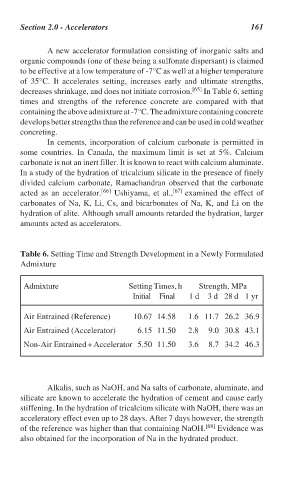
decreases shrinkage, and does not initiate corrosion. [65] In Table 6, setting
times and strengths of the reference concrete are compared with that
containing the above admixture at -7°C. The admixture containing concrete
develops better strengths than the reference and can be used in cold weather
concreting.
In cements, incorporation of calcium carbonate is permitted in
some countries. In Canada, the maximum limit is set at 5%. Calcium
carbonate is not an inert filler. It is known to react with calcium aluminate.
In a study of the hydration of tricalcium silicate in the presence of finely
divided calcium carbonate, Ramachandran observed that the carbonate
acted as an accelerator. [66] Ushiyama, et al., [67] examined the effect of
carbonates of Na, K, Li, Cs, and bicarbonates of Na, K, and Li on the
hydration of alite. Although small amounts retarded the hydration, larger
amounts acted as accelerators.
Table 6. Setting Time and Strength Development in a Newly Formulated
Admixture
Admixture Setting Times, h Strength, MPa
Initial Final 1 d 3 d 28 d 1 yr
Air Entrained (Reference) 10.67 14.58 1.6 11.7 26.2 36.9
Air Entrained (Accelerator) 6.15 11.50 2.8 9.0 30.8 43.1
Non-Air Entrained + Accelerator 5.50 11.50 3.6 8.7 34.2 46.3
Alkalis, such as NaOH, and Na salts of carbonate, aluminate, and
silicate are known to accelerate the hydration of cement and cause early
stiffening. In the hydration of tricalcium silicate with NaOH, there was an
acceleratory effect even up to 28 days. After 7 days however, the strength
of the reference was higher than that containing NaOH. [68] Evidence was
also obtained for the incorporation of Na in the hydrated product.