Page 231 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 231
200 Chapter Six
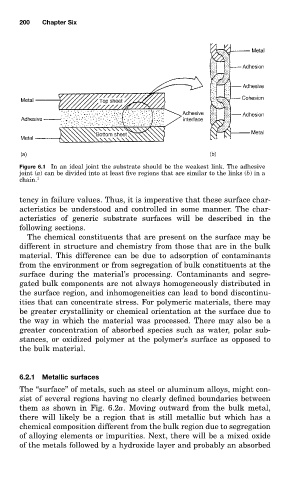
Figure 6.1 In an ideal joint the substrate should be the weakest link. The adhesive
joint (a) can be divided into at least five regions that are similar to the links (b)in a
chain. 1
tency in failure values. Thus, it is imperative that these surface char-
acteristics be understood and controlled in some manner. The char-
acteristics of generic substrate surfaces will be described in the
following sections.
The chemical constituents that are present on the surface may be
different in structure and chemistry from those that are in the bulk
material. This difference can be due to adsorption of contaminants
from the environment or from segregation of bulk constituents at the
surface during the material’s processing. Contaminants and segre-
gated bulk components are not always homogeneously distributed in
the surface region, and inhomogeneities can lead to bond discontinu-
ities that can concentrate stress. For polymeric materials, there may
be greater crystallinity or chemical orientation at the surface due to
the way in which the material was processed. There may also be a
greater concentration of absorbed species such as water, polar sub-
stances, or oxidized polymer at the polymer’s surface as opposed to
the bulk material.
6.2.1 Metallic surfaces
The ‘‘surface’’ of metals, such as steel or aluminum alloys, might con-
sist of several regions having no clearly defined boundaries between
them as shown in Fig. 6.2a. Moving outward from the bulk metal,
there will likely be a region that is still metallic but which has a
chemical composition different from the bulk region due to segregation
of alloying elements or impurities. Next, there will be a mixed oxide
of the metals followed by a hydroxide layer and probably an absorbed