Page 284 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 284
Surfaces and Surface Preparation 249
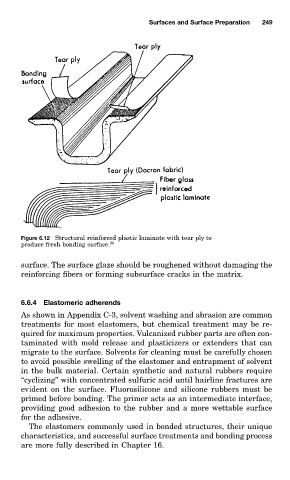
Figure 6.12 Structural reinforced plastic laminate with tear ply to
produce fresh bonding surface. 20
surface. The surface glaze should be roughened without damaging the
reinforcing fibers or forming subsurface cracks in the matrix.
6.6.4 Elastomeric adherends
As shown in Appendix C-3, solvent washing and abrasion are common
treatments for most elastomers, but chemical treatment may be re-
quired for maximum properties. Vulcanized rubber parts are often con-
taminated with mold release and plasticizers or extenders that can
migrate to the surface. Solvents for cleaning must be carefully chosen
to avoid possible swelling of the elastomer and entrapment of solvent
in the bulk material. Certain synthetic and natural rubbers require
‘‘cyclizing’’ with concentrated sulfuric acid until hairline fractures are
evident on the surface. Fluorosilicone and silicone rubbers must be
primed before bonding. The primer acts as an intermediate interface,
providing good adhesion to the rubber and a more wettable surface
for the adhesive.
The elastomers commonly used in bonded structures, their unique
characteristics, and successful surface treatments and bonding process
are more fully described in Chapter 16.