Page 536 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 536
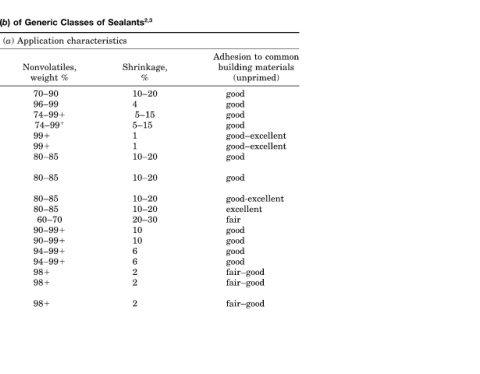
Adhesion to common building materials (unprimed) good good good good good–excellent good–excellent good good good-excellent excellent fair good good good good
Shrinkage, % 10–20 4 5–15 5–15 1 1 10–20 10–20 10–20 10–20 20–30 10 10 6 6 2 2 2
Application Characteristics (a) and Performance Capabilities (b) of Generic Classes of Sealants 2,3
(a) Application characteristics Nonvolatiles, weight % 70–90 96–99 74–99 74–99 99 99 80–85 80–85 80–85 80–85 60–70 90–99 90–99 94–99 94–99 98 98 98
Joint limits w d, in. 1 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 3 ⁄8 3 ⁄8 1 ⁄2 3 ⁄8 mastic thin beads 1 ⁄2 1 ⁄2 1 ⁄2 1 ⁄2 5 ⁄8 1 ⁄2 3 ⁄4 3 ⁄8 1 ⁄2 1 ⁄2 3 ⁄4 1 ⁄2
Cure type oxidation oxidation solvent rel. oxidation none thermoplastic water rel. water rel. solvent rel. solvent rel. solvent rel. catalyst cure catalyst cure
Generic type Butyl/polybutylene Emulsion acrylic (low One part polysulfide Two part polysulfide One part urethane Two part urethane Silicone structural (medium modulus)
TABLE 12.5 Oil base Oil resin base Butyl mastics Butyl curable Polyisobutylene Emulsion acrylic (high modulus) modulus) Hypalon Solvent acrylic Block copolymer Silicone