Page 539 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 539
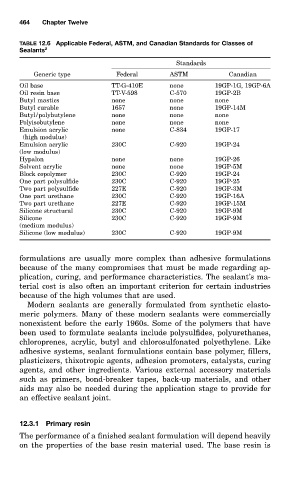
464 Chapter Twelve
TABLE 12.6 Applicable Federal, ASTM, and Canadian Standards for Classes of
Sealants 2
Standards
Generic type Federal ASTM Canadian
Oil base TT-G-410E none 19GP-1G, 19GP-6A
Oil resin base TT-V-598 C-570 19GP-2B
Butyl mastics none none none
Butyl curable 1657 none 19GP-14M
Butyl/polybutylene none none none
Polyisobutylene none none none
Emulsion acrylic none C-834 19GP-17
(high modulus)
Emulsion acrylic 230C C-920 19GP-24
(low modulus)
Hypalon none none 19GP-26
Solvent acrylic none none 19GP-5M
Block copolymer 230C C-920 19GP-24
One part polysulfide 230C C-920 19GP-25
Two part polysulfide 227E C-920 19GP-3M
One part urethane 230C C-920 19GP-16A
Two part urethane 227E C-920 19GP-15M
Silicone structural 230C C-920 19GP-9M
Silicone 230C C-920 19GP-9M
(medium modulus)
Silicone (low modulus) 230C C-920 19GP-9M
formulations are usually more complex than adhesive formulations
because of the many compromises that must be made regarding ap-
plication, curing, and performance characteristics. The sealant’s ma-
terial cost is also often an important criterion for certain industries
because of the high volumes that are used.
Modern sealants are generally formulated from synthetic elasto-
meric polymers. Many of these modern sealants were commercially
nonexistent before the early 1960s. Some of the polymers that have
been used to formulate sealants include polysulfides, polyurethanes,
chloroprenes, acrylic, butyl and chlorosulfonated polyethylene. Like
adhesive systems, sealant formulations contain base polymer, fillers,
plasticizers, thixotropic agents, adhesion promoters, catalysts, curing
agents, and other ingredients. Various external accessory materials
such as primers, bond-breaker tapes, back-up materials, and other
aids may also be needed during the application stage to provide for
an effective sealant joint.
12.3.1 Primary resin
The performance of a finished sealant formulation will depend heavily
on the properties of the base resin material used. The base resin is