Page 300 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 300
270 10 Carbons
Table 10.1 Application of carbon in aqueous batteries.
Battery Application of carbonaceous material
Lead-acid Bipolar current collector, electrode additive
Metal/air Air electrode, electrocatalyst support
Redox flow Positive electrode, negative electrode substrate, electrocatalyst
support, current collector, bipolar separator
Metal hydride/NiOOH Electrode additive
Hydrogen/NiOOH Electrode additive, electrocatalyst support
Cd/NiOOH Electrode additive
Zn/NiOOH Electrode additive
ZnAgO and Zn/Ag 2 O Electrode additive
Zn/HgO Electrode additive
Alkaline Zn/MnO 2 Electrode additive
Zinc/carbon (Leclanch´ e cell) Electrode additive, current collector
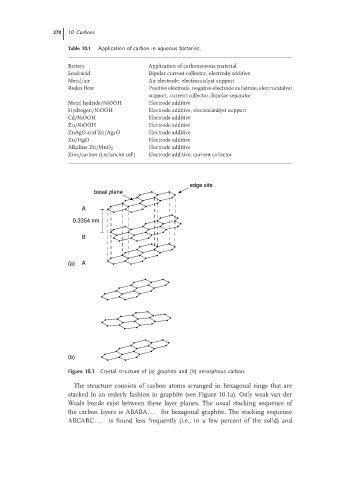
edge site
basal plane
A
0.3354 nm
B
(a) A
(b)
Figure 10.1 Crystal structure of (a) graphite and (b) amorphous carbon.
The structure consists of carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal rings that are
stacked in an orderly fashion in graphite (see Figure 10.1a). Only weak van der
Waals bonds exist between these layer planes. The usual stacking sequence of
the carbon layers is ABABA.. . for hexagonal graphite. The stacking sequence
ABCABC... is found less frequently (i.e., in a few percent of the solid) and