Page 424 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 424
396 13 Rechargeable Lithium Anodes
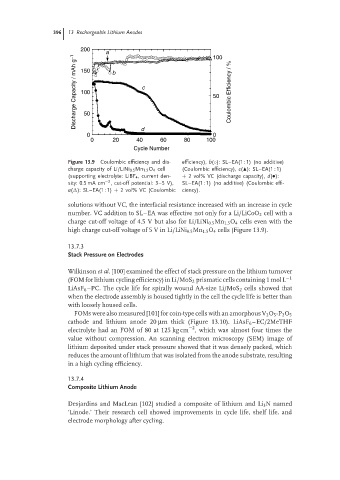
200 a 100
Discharge Capacity / mAh g −1 150 b c 50 Coulombic Efficiency / %
100
50
0 d 0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Cycle Number
Figure 13.9 Coulombic efficiency and dis- efficiency), b(◦): SL–EA(1 : 1) (no additive)
charge capacity of Li/LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 cell (Coulombic efficiency), c( ): SL–EA(1 : 1)
(supporting electrolyte: LiBF 4 , current den- + 2 vol% VC (discharge capacity), d(•):
−2
sity: 0.5 mA cm , cut-off potential: 3–5 V), SL–EA(1 : 1) (no additive) (Coulombic effi-
a( ): SL–EA(1 : 1) + 2 vol% VC (Coulombic ciency).
solutions without VC, the interfacial resistance increased with an increase in cycle
number. VC addition to SL–EA was effective not only for a Li/LiCoO 2 cell with a
charge cut-off voltage of 4.5 V but also for Li/LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 cells even with the
high charge cut-off voltage of 5 V in Li/LiNi 0.5 Mn 1.5 O 4 cells (Figure 13.9).
13.7.3
Stack Pressure on Electrodes
Wilkinson et al. [100] examined the effect of stack pressure on the lithium turnover
(FOM for lithium cycling efficiency) in Li/MoS 2 prismatic cells containing 1 mol L −1
LiAsF 6 –PC. The cycle life for spirally wound AA-size Li/MoS 2 cells showed that
when the electrode assembly is housed tightly in the cell the cycle life is better than
with loosely housed cells.
FOMs were also measured [101] for coin-type cells with an amorphous V 2 O 5 -P 2 O 5
cathode and lithium anode 20 µm thick (Figure 13.10). LiAsF 6 –EC/2MeTHF
−2
electrolyte had an FOM of 80 at 125 kg cm , which was almost four times the
value without compression. An scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of
lithium deposited under stack pressure showed that it was densely packed, which
reduces the amount of lithium that was isolated from the anode substrate, resulting
in a high cycling efficiency.
13.7.4
Composite Lithium Anode
Desjardins and MacLean [102] studied a composite of lithium and Li 3 N named
‘Linode.’ Their research cell showed improvements in cycle life, shelf life, and
electrode morphology after cycling.