Page 677 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 677
18.3 Hybrid Electrolytes 651
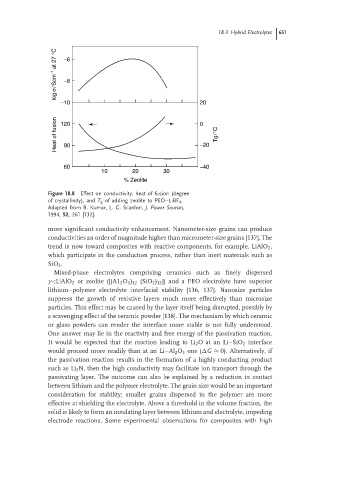
log σ/Scm -1 at 27 °C −6
−8
−10 20
Heat of fusion 120 0 Tg/°C
−20
90
60 −40
10 20 30
% Zeolite
Figure 18.8 Effect on conductivity, heat of fusion (degree
of crystallinity), and T g of adding zeolite to PEO–LiBF 4 .
Adapted from B. Kumar, L. G. Scanlon, J. Power Sources,
1994, 52, 261 [132].
more significant conductivity enhancement. Nanometer-size grains can produce
conductivities an order of magnitude higher than micrometer-size grains [137]. The
trend is now toward composites with reactive components, for example, LiAlO 2 ,
which participate in the conduction process, rather than inert materials such as
SiO 2 .
Mixed-phase electrolytes comprising ceramics such as finely dispersed
γ -;LiAlO 2 or zeolite ([(A1 2 O 3 ) 12 (SiO 2 ) 12 ]) and a PEO electrolyte have superior
lithium–polymer electrolyte interfacial stability [136, 137]. Nanosize particles
suppress the growth of resistive layers much more effectively than microsize
particles. This effect may be caused by the layer itself being disrupted, possibly by
a scavenging effect of the ceramic powder [138]. The mechanism by which ceramic
or glass powders can render the interface more stable is not fully understood.
One answer may lie in the reactivity and free energy of the passivation reaction.
It would be expected that the reaction leading to Li 2 Oatan Li–SiO 2 interface
would proceed more readily than at an Li–Al 2 O 3 one ( G ≈ 0). Alternatively, if
the passivation reaction results in the formation of a highly conducting product
such as Li 2 N, then the high conductivity may facilitate ion transport through the
passivating layer. The outcome can also be explained by a reduction in contact
between lithium and the polymer electrolyte. The grain size would be an important
consideration for stability; smaller grains dispersed in the polymer are more
effective at shielding the electrolyte. Above a threshold in the volume fraction, the
solid is likely to form an insulating layer between lithium and electrolyte, impeding
electrode reactions. Some experimental observations for composites with high