Page 85 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 85
2.5 Lithium Primary Batteries 51
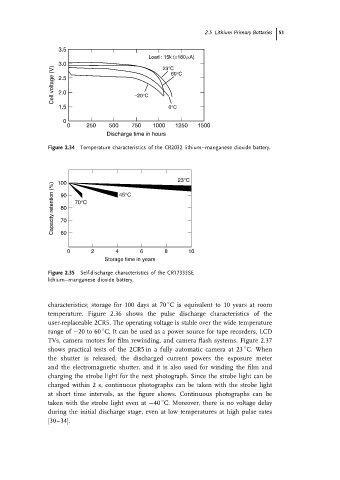
3.5
Load : 15k (≅180mA)
Cell voltage (V) 3.0 60°C
23°C
2.5
2.0
1.5 −20°C 0°C
0
0 250 500 750 1000 1250 1500
Discharge time in hours
Figure 2.34 Temperature characteristics of the CR2032 lithium–manganese dioxide battery.
23°C
100
Capacity retention (%) 90 70°C 45°C
80
70
60
0 2 4 6 8 10
Storage time in years
Figure 2.35 Self-discharge characteristics of the CR17335SE
lithium–manganese dioxide battery.
◦
characteristics; storage for 100 days at 70 C is equivalent to 10 years at room
temperature. Figure 2.36 shows the pulse discharge characteristics of the
user-replaceable 2CR5. The operating voltage is stable over the wide temperature
◦
range of −20 to 60 C. It can be used as a power source for tape recorders, LCD
TVs, camera motors for film rewinding, and camera flash systems. Figure 2.37
◦
shows practical tests of the 2CR5 in a fully automatic camera at 23 C. When
the shutter is released, the discharged current powers the exposure meter
and the electromagnetic shutter, and it is also used for winding the film and
charging the strobe light for the next photograph. Since the strobe light can be
charged within 2 s, continuous photographs can be taken with the strobe light
at short time intervals, as the figure shows. Continuous photographs can be
◦
taken with the strobe light even at −40 C. Moreover, there is no voltage delay
during the initial discharge stage, even at low temperatures at high pulse rates
[30–34].