Page 88 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 88
54 2 Practical Batteries
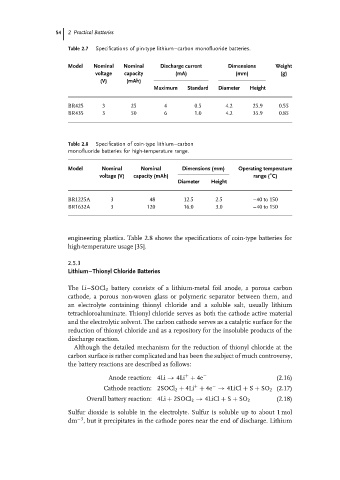
Table 2.7 Specifications of pin-type lithium–carbon monofluoride batteries.
Model Nominal Nominal Discharge current Dimensions Weight
voltage capacity (mA) (mm) (g)
(V) (mAh)
Maximum Standard Diameter Height
BR425 3 25 4 0.5 4.2 25.9 0.55
BR435 3 50 6 1.0 4.2 35.9 0.85
Table 2.8 Specification of coin-type lithium–carbon
monofluoride batteries for high-temperature range.
Model Nominal Nominal Dimensions (mm) Operating temperature
◦
voltage (V) capacity (mAh) range ( C)
Diameter Height
BR1225A 3 48 12.5 2.5 –40 to 150
BR1632A 3 120 16.0 3.0 –40 to 150
engineering plastics. Table 2.8 shows the specifications of coin-type batteries for
high-temperature usage [35].
2.5.3
Lithium–Thionyl Chloride Batteries
The Li–SOCl 2 battery consists of a lithium-metal foil anode, a porous carbon
cathode, a porous non-woven glass or polymeric separator between them, and
an electrolyte containing thionyl chloride and a soluble salt, usually lithium
tetrachloroaluminate. Thionyl chloride serves as both the cathode active material
and the electrolytic solvent. The carbon cathode serves as a catalytic surface for the
reduction of thionyl chloride and as a repository for the insoluble products of the
discharge reaction.
Although the detailed mechanism for the reduction of thionyl chloride at the
carbon surface is rather complicated and has been the subject of much controversy,
the battery reactions are described as follows:
Anode reaction: 4Li → 4Li + 4e − (2.16)
+
−
+
Cathode reaction: 2SOCl 2 + 4Li + 4e → 4LiCl + S + SO 2 (2.17)
Overall battery reaction: 4Li + 2SOCl 2 → 4LiCl + S + SO 2 (2.18)
Sulfur dioxide is soluble in the electrolyte. Sulfur is soluble up to about 1 mol
−3
dm , but it precipitates in the cathode pores near the end of discharge. Lithium