Page 33 - Handbook of Biomechatronics
P. 33
26 Ahmed R. Arshi
and possible expansion of the model has taken place, other issues such as
economics and industrial constraints could be addressed.
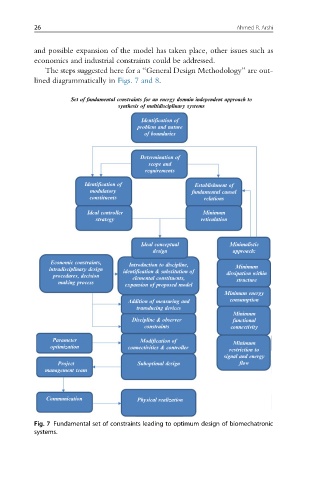
The steps suggested here for a “General Design Methodology” are out-
lined diagrammatically in Figs. 7 and 8.
Set of fundamental constraints for an energy domain independent approach to
synthesis of multidisciplinary systems
Identification of
problem and nature
of boundaries
Determination of
scope and
requirements
Identification of Establishment of
modulatory fundamental causal
constituents relations
Ideal controller Minimum
strategy reticulation
Ideal conceptual Minimalistic
design approach:
Economic constraints, Introduction to discipline,
intradisciplinary design identification & substitution of Minimum
procedures, decision elemental constituents, dissipation within
making process expansion of proposed model structure
Minimum energy
Addition of measuring and consumption
transducing devices
Minimum
Discipline & observer functional
constraints connectivity
Parameter Modification of Minimum
optimization connectivities & controller restriction to
signal and energy
Project Suboptimal design flow
management team
Communication Physical realization
Fig. 7 Fundamental set of constraints leading to optimum design of biomechatronic
systems.