Page 28 - Handbook of Biomechatronics
P. 28
Introduction 21
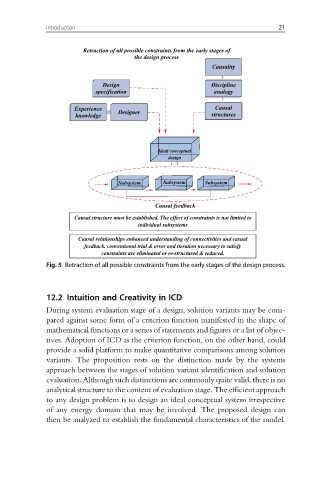
Retraction of all possible constraints from the early stages of
the design process
Causality
Design Discipline
specification analogy
Experience Designer Causal
knowledge structures
Ideal conceptual
design
Subsystem Subsystem Subsystem
Causal feedback
Causal structure must be established. The effect of constraints is not limited to
individual subsystems
Causal relationships enhanced understanding of connectivities and casual
feedback. conventional trial & error and iteration necessary to satisfy
constraints are eliminated or re-structured & reduced.
Fig. 5 Retraction of all possible constraints from the early stages of the design process.
12.2 Intuition and Creativity in ICD
During system evaluation stage of a design, solution variants may be com-
pared against some form of a criterion function manifested in the shape of
mathematical functions or a series of statements and figures or a list of objec-
tives. Adoption of ICD as the criterion function, on the other hand, could
provide a solid platform to make quantitative comparisons among solution
variants. The proposition rests on the distinction made by the systems
approach between the stages of solution variant identification and solution
evaluation. Although such distinctions are commonly quite valid, there is no
analytical structure to the content of evaluation stage. The efficient approach
to any design problem is to design an ideal conceptual system irrespective
of any energy domain that may be involved. The proposed design can
then be analyzed to establish the fundamental characteristics of the model.