Page 40 - Handbook of Biomechatronics
P. 40
34 Reva E. Johnson and Jonathon W. Sensinger
Peak torque
Brushless DC electric motor
Torque/speed characteristics
Torque
Intermittent
torque
Rated torque
Continuous
torque zone
Rated speed Maximum speed
Speed
(A)
Motor envelope
3
2
Speed (rad/s) –1 1 0 Envelope
Positioning arm
Moving light load
Moving heavy load
–2
–3
–10 –5 0 5 10
(B) Torque (Nm)
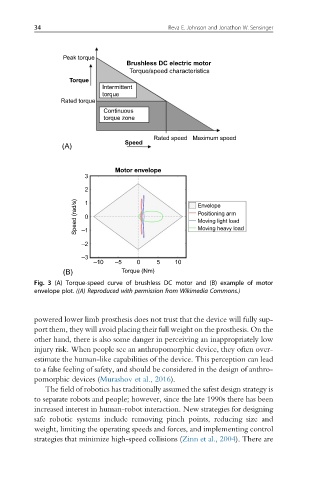
Fig. 3 (A) Torque-speed curve of brushless DC motor and (B) example of motor
envelope plot. ((A) Reproduced with permission from Wikimedia Commons.)
powered lower limb prosthesis does not trust that the device will fully sup-
port them, they will avoid placing their full weight on the prosthesis. On the
other hand, there is also some danger in perceiving an inappropriately low
injury risk. When people see an anthropomorphic device, they often over-
estimate the human-like capabilities of the device. This perception can lead
to a false feeling of safety, and should be considered in the design of anthro-
pomorphic devices (Murashov et al., 2016).
The field of robotics has traditionally assumed the safest design strategy is
to separate robots and people; however, since the late 1990s there has been
increased interest in human-robot interaction. New strategies for designing
safe robotic systems include removing pinch points, reducing size and
weight, limiting the operating speeds and forces, and implementing control
strategies that minimize high-speed collisions (Zinn et al., 2004). There are