Page 232 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 232
Chapter 8 A review on plant diseases recognition through deep learning 223
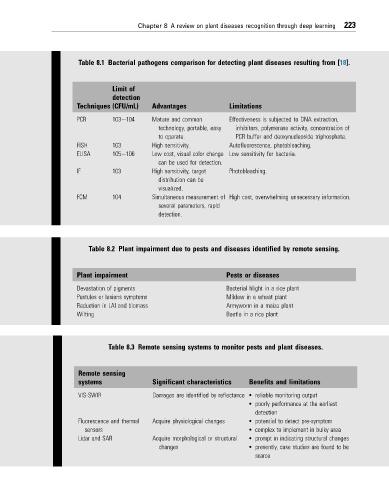
Table 8.1 Bacterial pathogens comparison for detecting plant diseases resulting from [18].
Limit of
detection
Techniques (CFU/mL) Advantages Limitations
PCR 103e104 Mature and common Effectiveness is subjected to DNA extraction,
technology, portable, easy inhibitors, polymerase activity, concentration of
to operate. PCR buffer and deoxynucleoside triphosphate.
FISH 103 High sensitivity. Autofluorescence, photobleaching.
ELISA 105e106 Low cost, visual color change Low sensitivity for bacteria.
can be used for detection.
IF 103 High sensitivity, target Photobleaching.
distribution can be
visualized.
FCM 104 Simultaneous measurement of High cost, overwhelming unnecessary information.
several parameters, rapid
detection.
Table 8.2 Plant impairment due to pests and diseases identified by remote sensing.
Plant impairment Pests or diseases
Devastation of pigments Bacterial blight in a rice plant
Pustules or lesions symptoms Mildew in a wheat plant
Reduction in LAI and biomass Armyworm in a maize plant
Wilting Beetle in a rice plant
Table 8.3 Remote sensing systems to monitor pests and plant diseases.
Remote sensing
systems Significant characteristics Benefits and limitations
VIS-SWIR Damages are identified by reflectance • reliable monitoring output
• poorly performance at the earliest
detection
Fluorescence and thermal Acquire physiological changes • potential to detect pre-symptom
sensors • complex to implement in bulky area
Lidar and SAR Acquire morphological or structural • prompt in indicating structural changes
changes • presently, case studies are found to be
scarce