Page 42 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 42
30 Chapter 2 Deep convolutional neural network in medical image processing
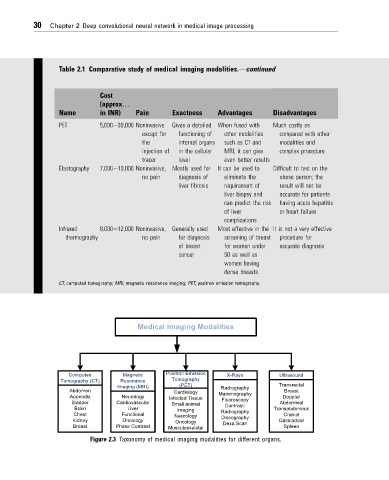
Table 2.1 Comparative study of medical imaging modalities.dcontinued
Cost
(approx.
Name in INR) Pain Exactness Advantages Disadvantages
PET 5,000e30,000 Noninvasive Gives a detailed When fused with Much costly as
except for functioning of other modalities compared with other
the internal organs such as CT and modalities and
injection of in the cellular MRI, it can give complex procedure
tracer level even better results
Elastography 7,000e10,000 Noninvasive, Mostly used for It can be used to Difficult to test on the
no pain diagnosis of eliminate the obese person; the
liver fibrosis requirement of result will not be
liver biopsy and accurate for patients
can predict the risk having acute hepatitis
of liver or heart failure
complications
Infrared 8,000e12,000 Noninvasive, Generally used Most effective in the It is not a very effective
thermography no pain for diagnosis screening of breast procedure for
of breast for women under accurate diagnosis
cancer 50 as well as
women having
dense breasts
CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography.
Medical Imaging Modalities
Computed Magnetic Positron Emission X-Rays Ultrasound
Tomography (CT) Resonance Tomography
Imaging (MRI) (PET) Radiography Transrectal
Abdomen Cardiology Mammography Breast
Appendix Neurology Infected Tissue Fluoroscopy Doppler
Bladder Cardiovascular Small animal Contrast- Abdominal
Brain Liver imaging Transabdominal
Chest Functional Neurology Radiography Cranial
Kidney Oncology Oncology Discography Gallbladder
Dexa Scan
Breast Phase Contrast Musculoskeletal Spleen
Figure 2.3 Taxonomy of medical imaging modalities for different organs.