Page 19 - Handbook of Electronic Assistive Technology
P. 19
6 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRONIC ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY
In adolescence there is a massive reorganisation of pathways within the CNS; it’s like
someone has run into an old-fashioned telephone exchange, yanked all the wires out and
stuck them back completely higgledy-piggledy. fMRI allows us to see how our CNS circuits
mature, lighting up new organisations like Christmas lights in the teenage brain. Frankly,
it’s a miracle they can put one foot in front of the other, just when we expect them to start
doing complex exams.
Blood Supply
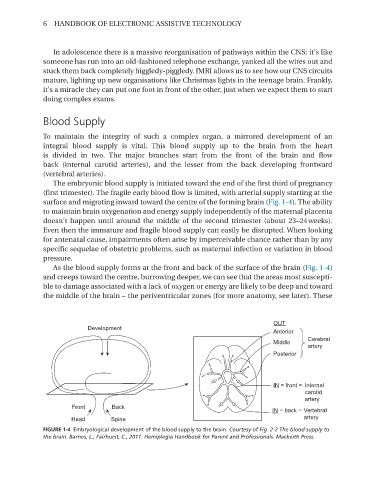
To maintain the integrity of such a complex organ, a mirrored development of an
integral blood supply is vital. This blood supply up to the brain from the heart
is divided in two. The major branches start from the front of the brain and flow
back (internal carotid arteries), and the lesser from the back developing frontward
(vertebral arteries).
The embryonic blood supply is initiated toward the end of the first third of pregnancy
(first trimester). The fragile early blood flow is limited, with arterial supply starting at the
surface and migrating inward toward the centre of the forming brain (Fig. 1-4). The ability
to maintain brain oxygenation and energy supply independently of the maternal placenta
doesn’t happen until around the middle of the second trimester (about 23–24 weeks).
Even then the immature and fragile blood supply can easily be disrupted. When looking
for antenatal cause, impairments often arise by imperceivable chance rather than by any
specific sequelae of obstetric problems, such as maternal infection or variation in blood
pressure.
As the blood supply forms at the front and back of the surface of the brain (Fig. 1-4)
and creeps toward the centre, burrowing deeper, we can see that the areas most suscepti-
ble to damage associated with a lack of oxygen or energy are likely to be deep and toward
the middle of the brain – the periventricular zones (for more anatomy, see later). These
OUT
Development
Anterior
Cerebral
Middle
artery
Posterior
IN = front = Internal
carotid
artery
Front Back
IN = back = Vertebral
Head Spine artery
FIGURE 1-4 Embryological development of the blood supply to the brain� Courtesy of Fig. 2-2 The blood supply to
the brain. Barnes, L., Fairhurst, C., 2011. Hemiplegia Handbook for Parent and Professionals. Mackeith Press.