Page 106 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 106
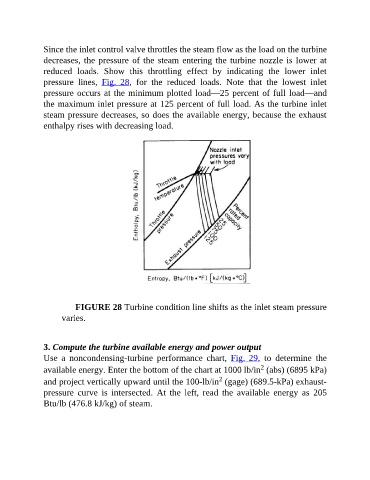
Since the inlet control valve throttles the steam flow as the load on the turbine
decreases, the pressure of the steam entering the turbine nozzle is lower at
reduced loads. Show this throttling effect by indicating the lower inlet
pressure lines, Fig. 28, for the reduced loads. Note that the lowest inlet
pressure occurs at the minimum plotted load—25 percent of full load—and
the maximum inlet pressure at 125 percent of full load. As the turbine inlet
steam pressure decreases, so does the available energy, because the exhaust
enthalpy rises with decreasing load.
FIGURE 28 Turbine condition line shifts as the inlet steam pressure
varies.
3. Compute the turbine available energy and power output
Use a noncondensing-turbine performance chart, Fig. 29, to determine the
2
available energy. Enter the bottom of the chart at 1000 lb/in (abs) (6895 kPa)
2
and project vertically upward until the 100-lb/in (gage) (689.5-kPa) exhaust-
pressure curve is intersected. At the left, read the available energy as 205
Btu/lb (476.8 kJ/kg) of steam.