Page 174 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 174
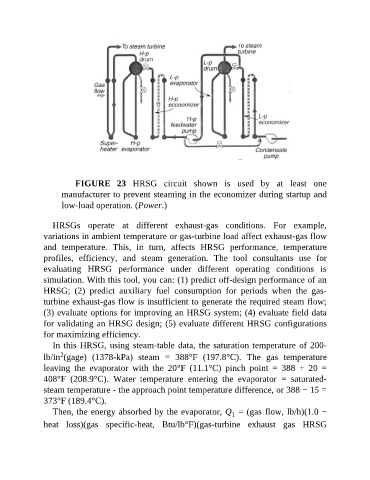
FIGURE 23 HRSG circuit shown is used by at least one
manufacturer to prevent steaming in the economizer during startup and
low-load operation. (Power.)
HRSGs operate at different exhaust-gas conditions. For example,
variations in ambient temperature or gas-turbine load affect exhaust-gas flow
and temperature. This, in turn, affects HRSG performance, temperature
profiles, efficiency, and steam generation. The tool consultants use for
evaluating HRSG performance under different operating conditions is
simulation. With this tool, you can: (1) predict off-design performance of an
HRSG; (2) predict auxiliary fuel consumption for periods when the gas-
turbine exhaust-gas flow is insufficient to generate the required steam flow;
(3) evaluate options for improving an HRSG system; (4) evaluate field data
for validating an HRSG design; (5) evaluate different HRSG configurations
for maximizing efficiency.
In this HRSG, using steam-table data, the saturation temperature of 200-
2
lb/in (gage) (1378-kPa) steam = 388°F (197.8°C). The gas temperature
leaving the evaporator with the 20°F (11.1°C) pinch point = 388 + 20 =
408°F (208.9°C). Water temperature entering the evaporator = saturated-
steam temperature - the approach point temperature difference, or 388 − 15 =
373°F (189.4°C).
Then, the energy absorbed by the evaporator, Q = (gas flow, lb/h)(1.0 −
1
heat loss)(gas specific-heat, Btu/lb°F)(gas-turbine exhaust gas HRSG