Page 291 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 291
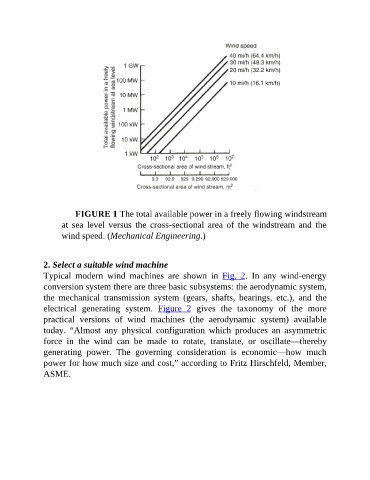
FIGURE 1 The total available power in a freely flowing windstream
at sea level versus the cross-sectional area of the windstream and the
wind speed. (Mechanical Engineering.)
2. Select a suitable wind machine
Typical modern wind machines are shown in Fig. 2. In any wind-energy
conversion system there are three basic subsystems: the aerodynamic system,
the mechanical transmission system (gears, shafts, bearings, etc.), and the
electrical generating system. Figure 2 gives the taxonomy of the more
practical versions of wind machines (the aerodynamic system) available
today. “Almost any physical configuration which produces an asymmetric
force in the wind can be made to rotate, translate, or oscillate—thereby
generating power. The governing consideration is economic—how much
power for how much size and cost,” according to Fritz Hirschfeld, Member,
ASME.