Page 123 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 123
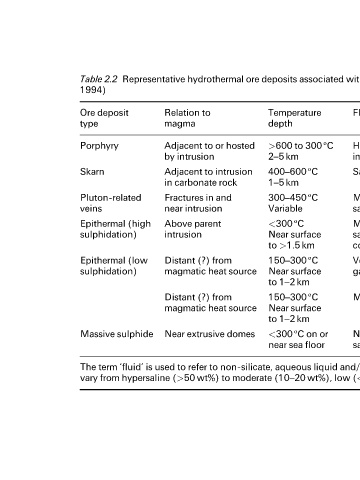
Table 2.2 Representative hydrothermal ore deposits associated with subduction related magmatism (after Hedenquist and Lowenstern,
1994)
Ore deposit Relation to Temperature Fluid Associated Example of
type magma depth metals active analogue
Porphyry Adjacent to or hosted >600 to 300 ëC Hypersaline and Cu Mo Au, Shallow magma bodies
by intrusion 2±5 km immiscible vapour Mo, W or Sn beneath stratovolcano
Skarn Adjacent to intrusion 400±600ëC Saline to moderate Fe, Cu, Sn, W, Mo, Shallow magma bodies
in carbonate rock 1±5 km Au, Ag, Pb-Zn beneath stratovolcano
Pluton-related Fractures in and 300±450ëC Moderate to low Sn, W, Mo Pb-Zn, Shallow magma bodies
veins near intrusion Variable salinity Cu, Au beneath stratovolcano
Epithermal (high Above parent <300 ëC Moderate to low Au-Cu High-temperature fumaroles
sulphidation) intrusion Near surface salinity, early acidic Ag-Pb and acidic springs near
to >1.5 km condensate volcanic vent
Epithermal (low Distant (?) from 150±300 ëC Very low salinity, Au(Ag, Pb-Zn) Geothermal systems with
sulphidation) magmatic heat source Near surface gas-rich, neutral pH neutral pH hot springs,
to 1±2 km mud pools
Distant (?) from 150±300 ëC Moderate salinity Ag-Pb-Zn(Au) Not observed,
magmatic heat source Near surface transient brine?
to 1±2 km
Massive sulphide Near extrusive domes <300 ëC on or Near seawater Zn-Pb-Ag Back-arc seafloor vents,
near sea floor salinity, gas-rich (Cu or Au) black smokers
The term `fluid' is used to refer to non-silicate, aqueous liquid and/or vapour. The salinities (Na, K chloride) of fluids in these environments
vary from hypersaline (>50 wt%) to moderate (10±20 wt%), low (<5 wt%) and very low (0.2±0.5 wt%) salinity.