Page 128 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 128
Geology of gold ore deposits 107
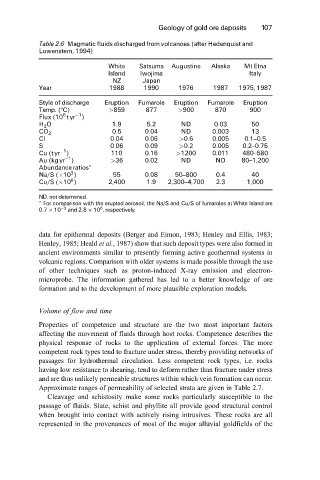
Table 2.6 Magmatic fluids discharged from volcanoes (after Hedenquist and
Lowenstern, 1994)
White Satsuma Augustine Alaska Mt Etna
Island Iwojima Italy
NZ Japan
Year 1988 1990 1976 1987 1975, 1987
Style of discharge Eruption Fumarole Eruption Fumarole Eruption
Temp. (ëC) >859 877 >900 870 900
ÿ1
6
Flux (10 t yr )
H 2 O 1.9 5.2 ND 0.03 50
0.5 0.04 ND 0.003 13
CO 2
Cl 0.04 0.06 >0.6 0.005 0.1±0.5
S 0.06 0.09 >0.2 0.005 0.2±0.75
ÿ1
Cu (tyr ) 110 0.16 >1200 0.011 480±580
ÿ1
Au (kg yr ) >36 0.02 ND ND 80±1,200
Abundance ratios*
3
Na/S ( 10 ) 55 0.08 50±800 0.4 40
6
Cu/S ( 10 ) 2,400 1.9 2,300±4,700 2.3 1,000
ND, not determined.
* For comparison with the erupted aerosoil, the Na/S and Cu/S of fumaroles at White Island are
6
0:7 10 ÿ3 and 2:8 10 , respectively.
data for epithermal deposits (Berger and Eimon, 1983; Henley and Ellis, 1983;
Henley, 1985; Heald et al., 1987) show that such deposit types were also formed in
ancient environments similar to presently forming active geothermal systems in
volcanic regions. Comparison with older systems is made possible through the use
of other techniques such as proton-induced X-ray emission and electron-
microprobe. The information gathered has led to a better knowledge of ore
formation and to the development of more plausible exploration models.
Volume of flow and time
Properties of competence and structure are the two most important factors
affecting the movement of fluids through host rocks. Competence describes the
physical response of rocks to the application of external forces. The more
competent rock types tend to fracture under stress, thereby providing networks of
passages for hydrothermal circulation. Less competent rock types, i.e. rocks
having low resistance to shearing, tend to deform rather than fracture under stress
and are thus unlikely permeable structures within which vein formation can occur.
Approximate ranges of permeability of selected strata are given in Table 2.7.
Cleavage and schistosity make some rocks particularly susceptible to the
passage of fluids. Slate, schist and phyllite all provide good structural control
when brought into contact with actively rising intrusives. These rocks are all
represented in the provenances of most of the major alluvial goldfields of the