Page 126 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 126
Geology of gold ore deposits 105
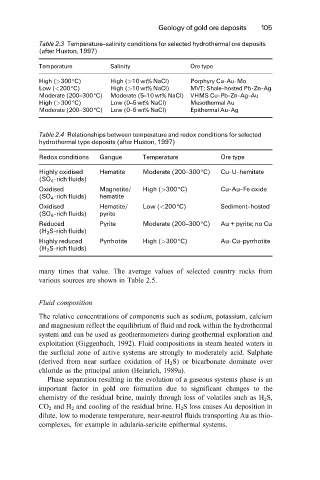
Table 2.3 Temperature±salinity conditions for selected hydrothermal ore deposits
(after Huston, 1997)
Temperature Salinity Ore type
High (>300 ëC) High (>10wt% NaCl) Porphyry Cu-Au-Mo
Low (<200ëC) High (>10wt% NaCl) MVT; Shale-hosted Pb-Zn-Ag
Moderate (200±300ëC) Moderate (5±10wt% NaCl) VHMS Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag-Au
High (>300 ëC) Low (0±5 wt% NaCl) Mesothermal Au
Moderate (200±300ëC) Low (0±5 wt% NaCl) Epithermal Au-Ag
Table 2.4 Relationships between temperature and redox conditions for selected
hydrothermal type deposits (after Huston, 1997)
Redox conditions Gangue Temperature Ore type
Highly oxidised Hematite Moderate (200±300 ëC) Cu-U-hemitate
(SO 4 -rich fluids)
Oxidised Magnetite/ High (>300 ëC) Cu-Au-Fe oxide
(SO 4 -rich fluids) hematite
Oxidised Hematite/ Low (<200ëC) Sediment-hosted
(SO 4 -rich fluids) pyrite
Reduced Pyrite Moderate (200±300 ëC) Au + pyrite; no Cu
(H 2 S-rich fluids)
Highly reduced Pyrrhotite High (>300 ëC) Au-Cu-pyrrhotite
(H 2 S-rich fluids)
many times that value. The average values of selected country rocks from
various sources are shown in Table 2.5.
Fluid composition
The relative concentrations of components such as sodium, potassium, calcium
and magnesium reflect the equilibrium of fluid and rock within the hydrothermal
system and can be used as geothermometers during geothermal exploration and
exploitation (Giggenbach, 1992). Fluid compositions in steam heated waters in
the surficial zone of active systems are strongly to moderately acid. Sulphate
(derived from near surface oxidation of H 2 S) or bicarbonate dominate over
chloride as the principal anion (Heinrich, 1989a).
Phase separation resulting in the evolution of a gaseous systems phase is an
important factor in gold ore formation due to significant changes to the
chemistry of the residual brine, mainly through loss of volatiles such as H 2 S,
CO 2 and H 2 and cooling of the residual brine. H 2 S loss causes Au deposition in
dilute, low to moderate temperature, near-neutral fluids transporting Au as thio-
complexes, for example in adularia-sericite epithermal systems.