Page 107 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 107
102 CHAPTER 5 Failure analysis of reinforced concrete structures
Node j Element i Node k
D s
M d
V d
h
V d
M d
L b
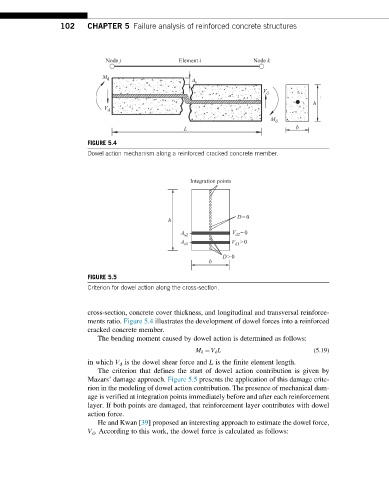
FIGURE 5.4
Dowel action mechanism along a reinforced cracked concrete member.
Integration points
D=0
h
A s2 V =0
d2
A s1 V d1 >0
D>0
b
FIGURE 5.5
Criterion for dowel action along the cross-section.
cross-section, concrete cover thickness, and longitudinal and transversal reinforce-
ments ratio. Figure 5.4 illustrates the development of dowel forces into a reinforced
cracked concrete member.
The bending moment caused by dowel action is determined as follows:
M d ¼ V d L (5.19)
in which V d is the dowel shear force and L is the finite element length.
The criterion that defines the start of dowel action contribution is given by
Mazars’ damage approach. Figure 5.5 presents the application of this damage crite-
rion in the modeling of dowel action contribution. The presence of mechanical dam-
age is verified at integration points immediately before and after each reinforcement
layer. If both points are damaged, that reinforcement layer contributes with dowel
action force.
He and Kwan [39] proposed an interesting approach to estimate the dowel force,
V d . According to this work, the dowel force is calculated as follows: