Page 318 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 318
4 Cutting Wear Particles 315
20µm 20µm
(a) (b)
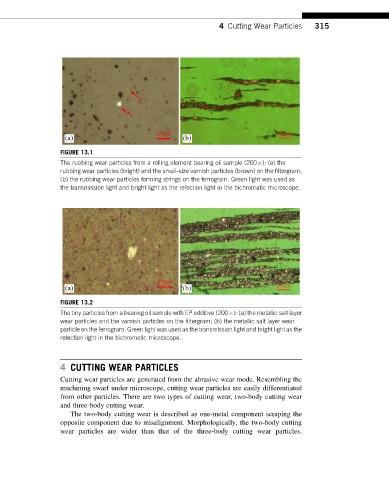
FIGURE 13.1
The rubbing wear particles from a rolling element bearing oil sample (200 ): (a) the
rubbing wear particles (bright) and the small-size varnish particles (brown) on the filtergram;
(b) the rubbing wear particles forming strings on the ferrogram. Green light was used as
the transmission light and bright light as the refection light in the bichromatic microscope.
20µm
(a) (b) 20µm
FIGURE 13.2
The tiny particles from a bearing oil sample with EP additive (200 ): (a) the metallic salt layer
wear particles and the varnish particles on the filtergram; (b) the metallic salt layer wear
particle on the ferrogram. Green light was used as the transmission light and bright light as the
refection light in the bichromatic microscope.
4 CUTTING WEAR PARTICLES
Cutting wear particles are generated from the abrasive wear mode. Resembling the
machining swarf under microscope, cutting wear particles are easily differentiated
from other particles. There are two types of cutting wear, two-body cutting wear
and three-body cutting wear.
The two-body cutting wear is described as one-metal component scraping the
opposite component due to misalignment. Morphologically, the two-body cutting
wear particles are wider than that of the three-body cutting wear particles.