Page 18 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 18
INTRODUCTION TO POLYMERS AND PLASTICS
1.4 CHAPTER 1
polymers. Polymers synthesized by this method typically have atoms other than carbon in
the backbone. Examples include polyesters and polyamides.
Chain-reaction polymerizations (also referred to as addition polymerizations) require
an initiator for polymerization to occur. Initiation can occur by a free radical, an anionic,
or a cationic species. These initiators open the double bond of a vinyl monomer, and the
reaction proceeds as shown above in Fig. 1.1. Chain-reaction polymers typically contain
only carbon in their backbone and include such polymers as polystyrene and polyvinyl
chloride.
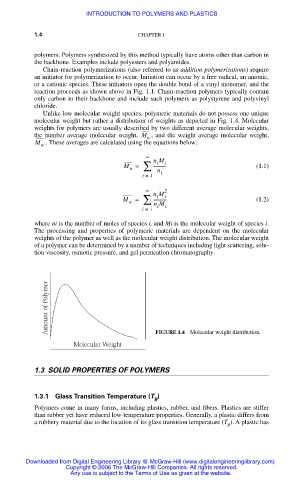
Unlike low molecular weight species, polymeric materials do not possess one unique
molecular weight but rather a distribution of weights as depicted in Fig. 1.4. Molecular
weights for polymers are usually described by two different average molecular weights,
the number average molecular weight, M , and the weight average molecular weight,
n
M . These averages are calculated using the equations below:
w
∞
n ∑ n M i
i
M = ----------- (1.1)
n
i = 1 i
∞ n M 2
w ∑ i i
M = ------------ (1.2)
n M i
i
i = 1
where ni is the number of moles of species i, and Mi is the molecular weight of species i.
The processing and properties of polymeric materials are dependent on the molecular
weights of the polymer as well as the molecular weight distribution. The molecular weight
of a polymer can be determined by a number of techniques including light scattering, solu-
tion viscosity, osmotic pressure, and gel permeation chromatography.
FIGURE 1.4 Molecular weight distribution.
1.3 SOLID PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS
1.3.1 Glass Transition Temperature (T )
g
Polymers come in many forms, including plastics, rubber, and fibers. Plastics are stiffer
than rubber yet have reduced low-temperature properties. Generally, a plastic differs from
a rubbery material due to the location of its glass transition temperature (T ). A plastic has
g
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.